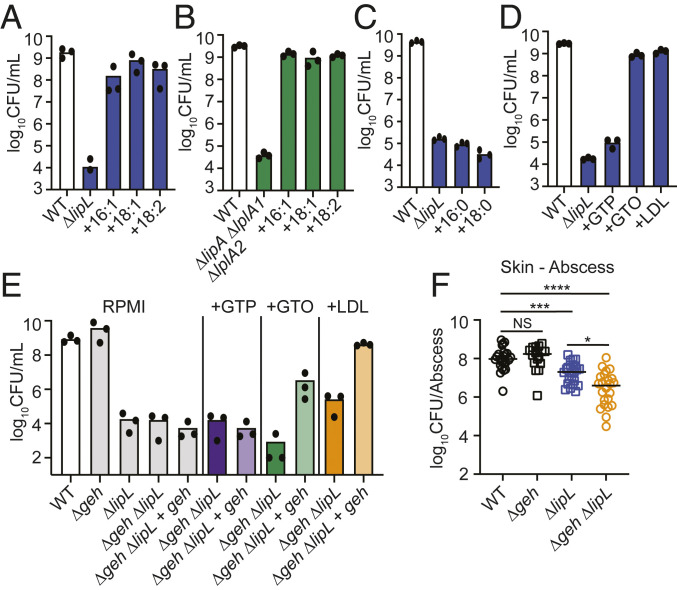
Fig. 3.
UFA substrates bypass requirement for lipoic acid by S. aureus. (A and B) 24 h subculture growth (log10 CFU/mL) of (A) ΔlipL and (B) ΔlipA ΔlplA1 ΔlplA2 strains in RPMI only or RPMI supplemented with 50 μM of each palmitoleic acid (16:1), oleic acid (18:1), or linoleic acid (18:2). (C and D) 24 h subculture growth (log10 CFU/mL) of ΔlipL strain in RPMI supplemented with (C) saturated FAs [50 μM palmitic acid (16:0) or 50 μM stearic acid (18:0)] or (D) covalently bound FA substrates (16.67 μM GTP, 16.67 μM GTO, or 0.34 mg/mL human LDL). (E) 24 h subculture growth (log10 CFU/mL) of Δgeh ΔlipL and Δgeh ΔlipL + lipL strains in RPMI supplemented with GTP, GTO, or LDL as indicated in (D). WT Δgeh, ΔlipL, Δgeh ΔlipL, and Δgeh ΔlipL + lipL strains were grown in RPMI without lipid supplementation as controls. (F) Bacterial burden (log10 CFU) in skin abscesses of mice at 120 h postinfection with 1 × 107 CFU WT (n = 24), Δgeh (n = 16), ΔlipL (n = 24), and Δgeh ΔlipL (n = 24) strains. P values were determined by a nonparametric one-way ANOVA (Kruskal–Wallis test) with Dunn’s posttest. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.