Fig. 2. Structural details of GABAB in the inactive apo state.
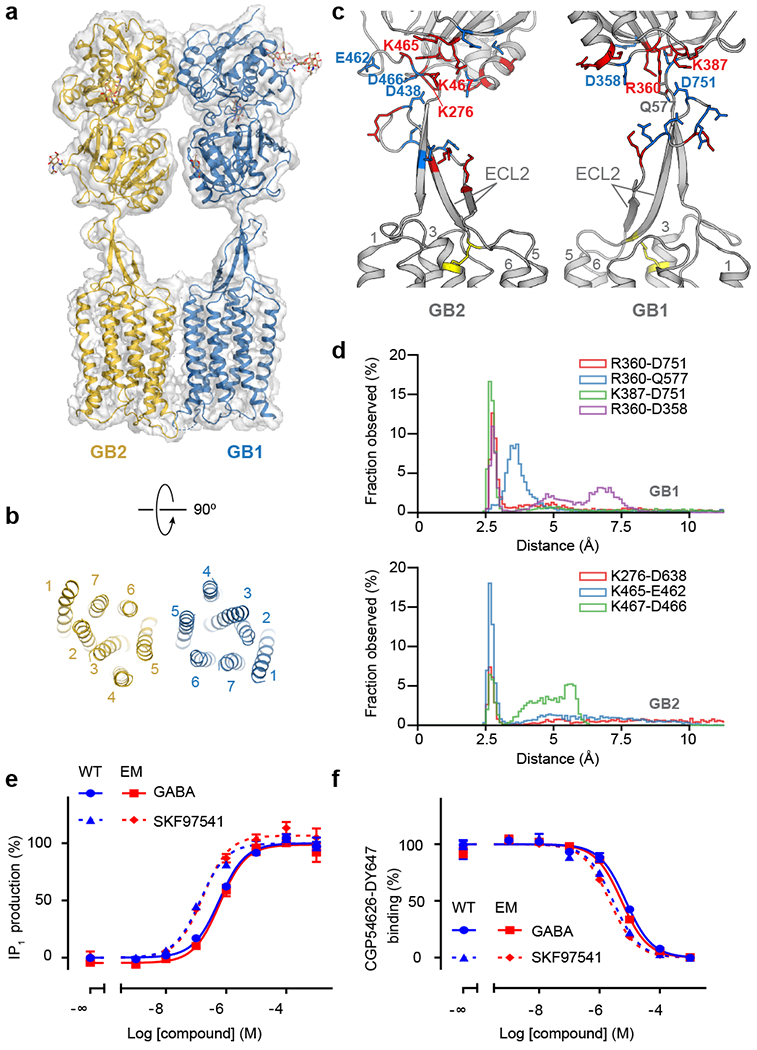
a, Overall view of the apo GABAB model and map. b, Extracellular view of the GABAB TMD in the inactive apo state. c, Structure of the stalk domains. The junctions between the stalks and the VFTs are stabilized by a network of electrostatic interactions between positively (red) and negatively (blue) charged residues. The disulfide bond between ECL2 and TM3 is shown as yellow sticks. d, Distribution of distances for ionic interactions between the stalk and VFT in GB1 and GB2 obtained from MD simulations of apo GABAB. e, IP1 production mediated by the WT receptor (blue) or the construct used for cryo-EM (red) upon stimulation with GABA (solid line) or SKF97541 (dotted line). f, Displacement of non-permeant antagonist CGP54626-DY647 by GABA (solid line) or SKF97541 (dotted line) from the WT receptor (blue) or the construct used for cryo-EM (red). Data shown in (e) and (f) are normalized by the WT response and presented as means ± SEM of 4 biologically independent experiments.
