Extended Data Fig. 1 |. Expression, characterization and purification of GABAB.
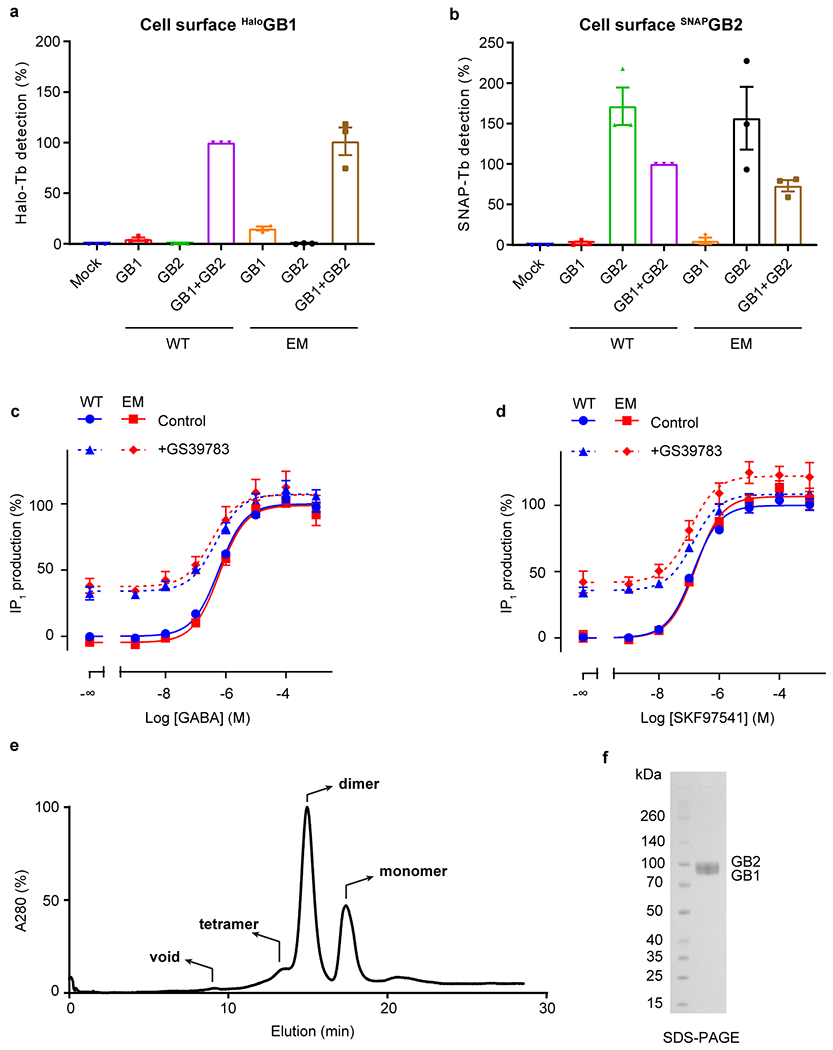
a, b, Cell surface expression of Halo-GB1 (a) and SNAP-GB2 (b) transfected alone or co-transfected with the second subunit, measured by the fluorescence emission of the Lumi4-Tb bound to the Halo- (a) or SNAP-tag (b). Values are normalized by the WT GB1 co-transfected with WT GB2 (purple bar) and shown as means ± SD of 3 biologically independent experiments. GABAB constructs for cryo-EM are expressed and function like the wild-type receptor. c, d, Positive allosteric effect of GS39783 (5 μM) on IP1 accumulation in cells expressing WT or cryo-EM constructs of GABAB receptor heterodimers and activated either by (c) GABA or (d) SKF97541. Data are normalized by the WT response in absence of GS39783 (Control) and shown as means ± SEM of 3 biologically independent experiments (4 for WT). e, Representative size exclusion chromatography (SEC) profile of apo GABAB in digitonin micelles. Dimeric fractions were pooled, supplemented with ligand, and concentrated for cryo-EM imaging. f, Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE profile shows two distinct bands for GB1 (86 kDa) and GB2 (88 kDa). For gel source data, see Supplementary Figure 1.
