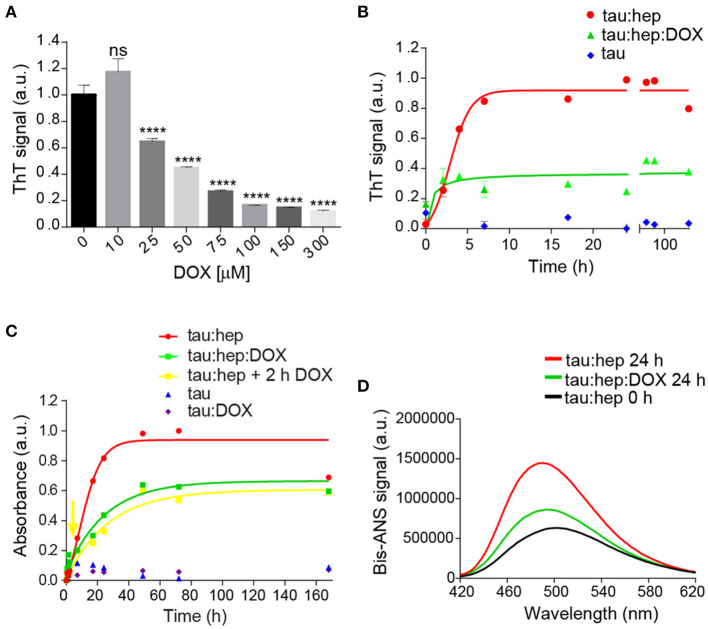
Figure 1.
Doxycycline affects tau canonical amyloid aggregation. (A) Dose-response of doxycycline over tau amyloid aggregation monitored by fluorescence emission intensity of 25 μM of thioflavin T in a solution containing samples of 22 μM tau, 0.2 mg/ml heparin and 10, 25, 75, 100, 150, or 300 μM of doxycycline. Samples were incubated at 37°C under orbital agitation and aggregation was assayed after 24 h. n = 3 ns: not significant. ****p ≤ 0.0001. Error bars represent SD. (B) Fluorescence emission intensity of 25 μM thioflavin T in a solution containing samples of tau 22 μM; 0.2 mg/ml heparin; and 100 μM of doxycycline. Samples were incubated at 37°C under orbital agitation and aggregation was assayed by ThT fluorescence emission. (C) Absorbance of 20 μM Congo Red in a solution containing samples of tau 22 μM; 0.2 mg/ml heparin; and 100 μM of doxycycline added at time 0 h (green line and squares) and at 2 h (yellow line and squares). Samples were incubated at 37°C under orbital agitation, and absorbance recorded on a TECAN Infinite M200 microplate reader. (D) Bis-ANS fluorescence signal of tau:heparin solution incubated 0 h (black line) and 24 h at 37°C under orbital agitation in the absence (red line) or presence of doxycycline (green line).