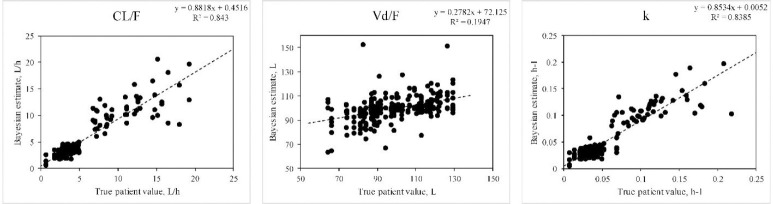
Fig. 3.
Ability of the Bayesian approach to estimate PKP when doses of a drug following a one-compartment model with linear elimination were given as various dosing regimens to simulated patients. Correlation between true values and the Bayesian estimates were significant (P < 0.01) for each parameter except for ka (not shown). Data represent 25 determinations for each of intravenous bolus, intermittent infusion, and oral dosing (single, multiple, and steady-state dosing) and continuous intravenous infusion. Data were estimated on sparse data (between 1, 2, or 3 blood fluid concentrations per subject). PKP, pharmacokinetic parameters; CL, clearance; Vd, volume of distribution.