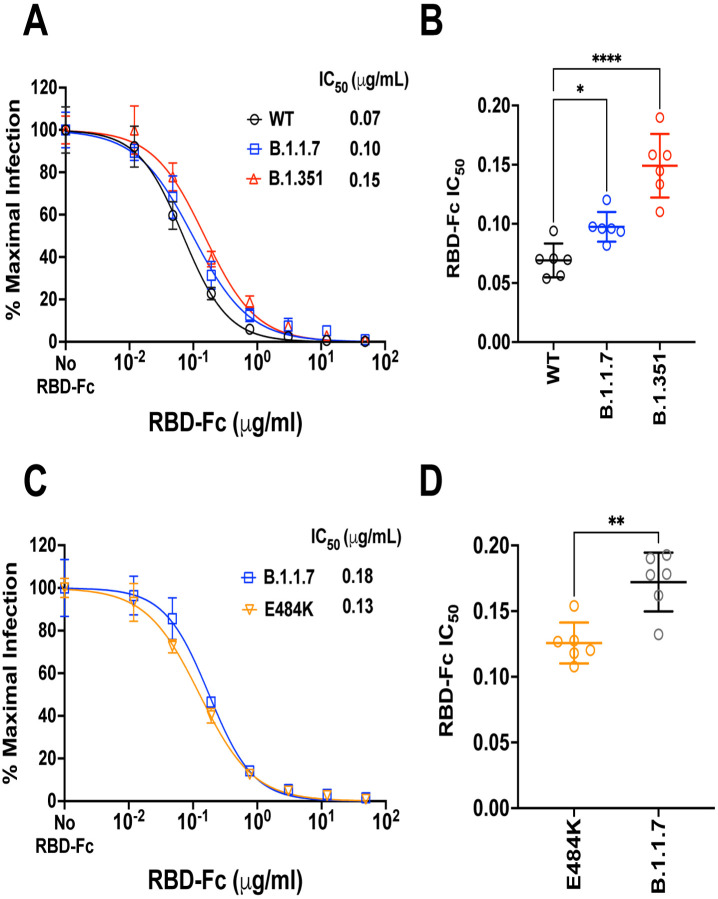
Figure 5. Competitive inhibition of rcVSV-CoV2-S entry by soluble RBD-Fc.
(A) Recombinant RBD-Fc was serially titrated with the infection inoculum containing a fixed amount of rcVSV-CoV2-S bearing WT or the indicated VOC spike proteins. 10 hpi, GFP+ cells were quantified by the Celigo image cytometer. Data points are means of six independent replicates with error bars representing S.D. The number of GFP+ cells in the absence of any RBD-Fc was set to 100% and used to normalize the infection response in the presence of increasing amounts of RBD-Fc. Log[inhibitor] versus normalized response variable slope nonlinear regression curves were generated using GraphPad PRISM (v9.1.0). (B) The IC50 values from each replicate dose response curve generated for a given virus were grouped. The mean (central bar) and SD (whiskers) for each group are indicated. Adjusted p values (*; p<0.05, **; p<0.01, ****; p<0.0001) from ordinary one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test are indicated. (C) is a repeat of the experiment done in A with the E484K mutant using a different preparation of recombinant RBD-Fc (see methods). B.1.1.7 serves as the common reference control. (D) The IC50 values were calculated and analyzed as in (B).