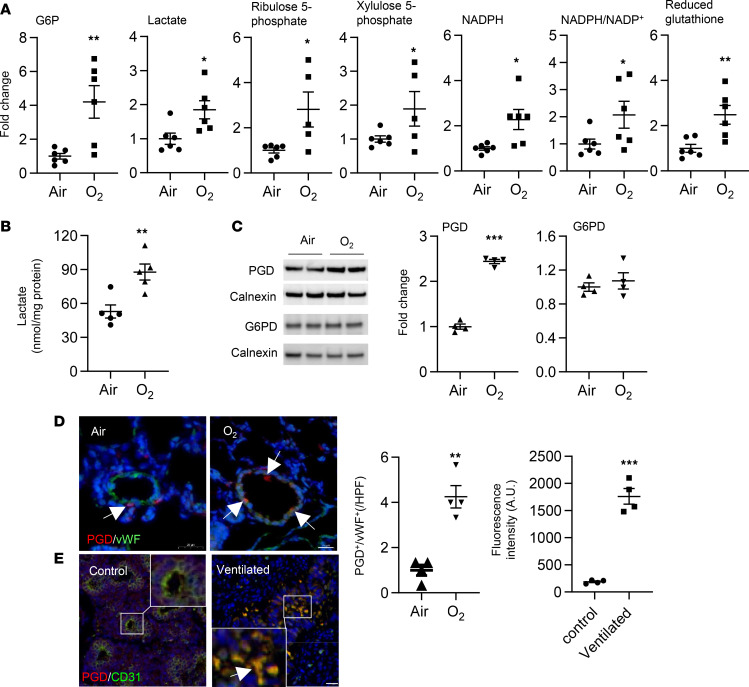
Figure 5. Glycolysis and the PPP are increased in lungs of mice exposed to hyperoxia, and endothelial PGD overexpression occurs in lungs of premature infants requiring mechanical ventilation.
(A–D) C57BL/6J neonatal mice (<12 hours old) were exposed to air or hyperoxia (95% O2) for 3 days and were then allowed to recover in room air until P7 (A) or P14 (B–D). (A) Untargeted metabolomics was performed by mass spectrometry in mouse lungs, and detectable metabolites in glycolysis and the PPP were presented. n = 6 per group. (B) Lactate levels were measured in mouse lungs using a L-lactate Assay kit. n = 5 per group. (C) Western blot was performed to assess protein levels of PGD and G6PD in mouse lungs. n = 4 per group. (D) Double immunofluorescence was conducted to determine the abundance of PGD in vWF+ cells in mouse lungs. Numbers of PGD+ and vWF+ cells were counted in 3 randomly selected high-power fields (HPF) for each sample, which was shown in left graph. Scale bar: 20 μm. n = 4 per group. (E) Immunofluorescence was carried out to detect colocalization of PGD and CD31 in lungs of premature infants requiring mechanical ventilation. Scale bar: 20 μm. Fluorescent intensity of PGD+/CD31+ cells was evaluated using an ImageJ software, which was shown in right graph. n = 4 per group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus air (A–D) or control subjects (E) using 1-tailed t test (A–E).