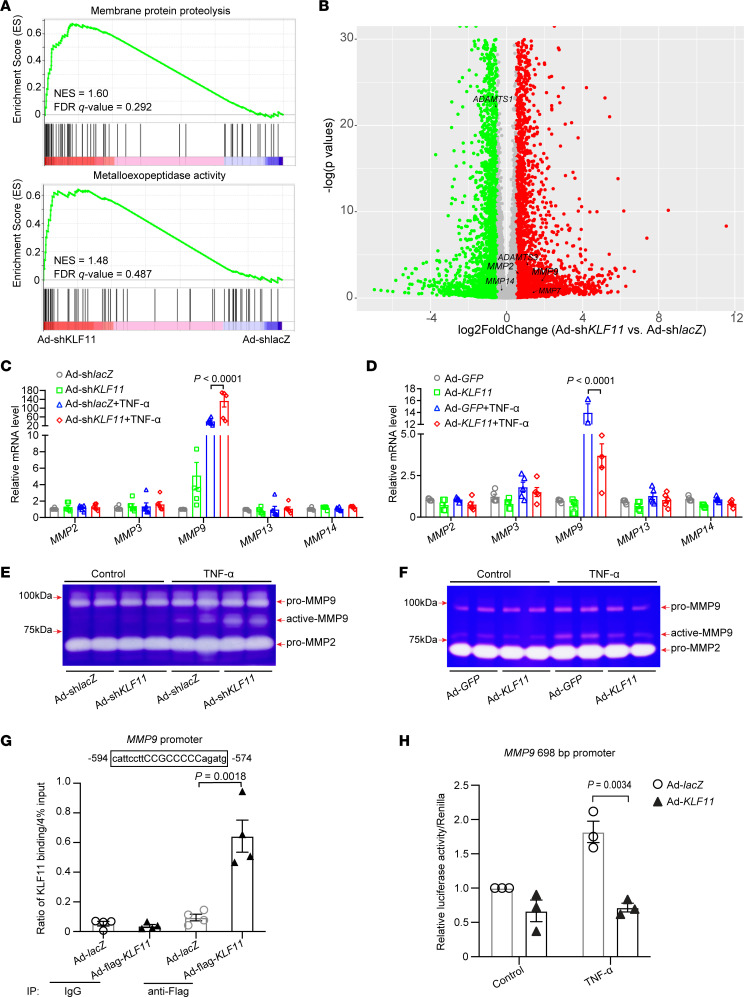
Figure 4. KLF11 inhibits MMP9 expression and activity in ECs.
(A and B) Human aortic ECs (HAECs) were infected with adenovirus carrying shRNA for KLF11 knockdown (Ad-shKLF11, 10 MOI, n = 4) or lacZ (Ad-shlacZ, n = 3) as control. After 48 hours, the total RNA was extracted for RNA sequencing. (A) The positive enrichment in the membrane protein proteolysis and metalloexopeptidase activity pathways is shown by gene set enrichment analysis plots (Ad-shKLF11 vs. Ad-shlacZ). NES, normalized enrichment score. (B) The differentially expressed genes (Ad-shKLF11 vs. Ad-shlacZ) are shown as volcano plots. Green dots, log2FoldChange < –0.5. Red dots, log2FoldChange > 0.5. Gray dots, –0.5 < log2FoldChange < 0.5. (C–F) HAECs were infected with Ad-shlacZ or Ad-shKLF11 or Ad-GFP or Ad-KLF11 (10 MOI). After 48 hours, they were treated with or without TNF-α (2 ng/mL) for 12 hours. (C and D) The mRNA levels of MMP2, MMP3, MMP9, MMP13, and MMP14 were determined by qPCR. (E and F) Representative gelatin zymography for the activity of MMP2 and MMP9 in the conditioned medium. Samples from E and F were run on 8% and 10% SDS-PAGE gels with 0.1% gelatin, respectively. (G) HAECs were infected with Ad-lacZ or Ad-flag-KLF11. After 48 hours, they were stimulated with TNF-α (2 ng/mL) for 4 hours. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay was performed using an antibody against flag or IgG. (H) Luciferase reporter assay in HAECs transfected with an MMP9 promoter-driven luciferase reporter containing a KLF11 binding site and infected with Ad-lacZ or Ad-KLF11. After 48 hours, they were stimulated with TNF-α (2 ng/mL) for 4 hours. The luciferase activity was normalized against that of cotransfected Renilla. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak post hoc analysis (C, D, G, and H).