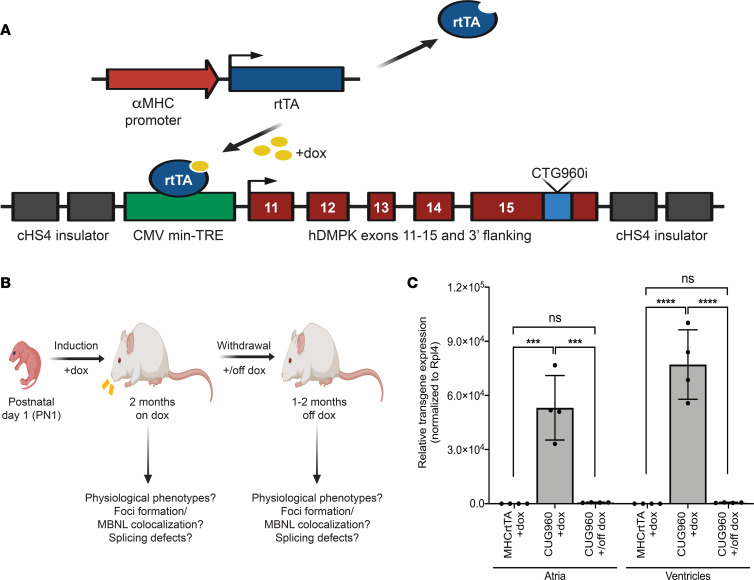
Figure 1. Bitransgenic mouse model for inducible and heart-specific expression of CUGexp RNA.
(A) The TREDT960I transgene consists of a minimal CMV promoter fused to a tetracycline response element regulating doxycycline induction of RNA containing 960 interrupted CUG repeats in the context of human DMPK exons 11–15. The expression of reverse tetracycline transactivator (rtTA) transgene is driven by a cardiomyocyte-specific α myosin heavy chain promoter. (B) Animals were given 2 g/kg dox food for induction of CUG repeat RNA expression beginning at PN1 and characterized for DM1-associated cardiac manifestations. Animals were switched to standard chow to evaluate reversal of disease features in response to cessation of CUGexp RNA expression. (C) RT-qPCR analysis of transgene mRNA expression in atria and ventricles of CUG960 mice in response to dox induction since PN1 for 2 months and withdrawal for 2 months in comparison with MHCrtTA +dox control mice. mRpl4 was used as an internal control for normalization. n = 4 animals per group. Data represent the mean ± SD and were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons. ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. CUGexp, expanded CUG repeat; DM1, myotonic dystrophy type 1; dox, doxycycline; PN1, postnatal day 1.