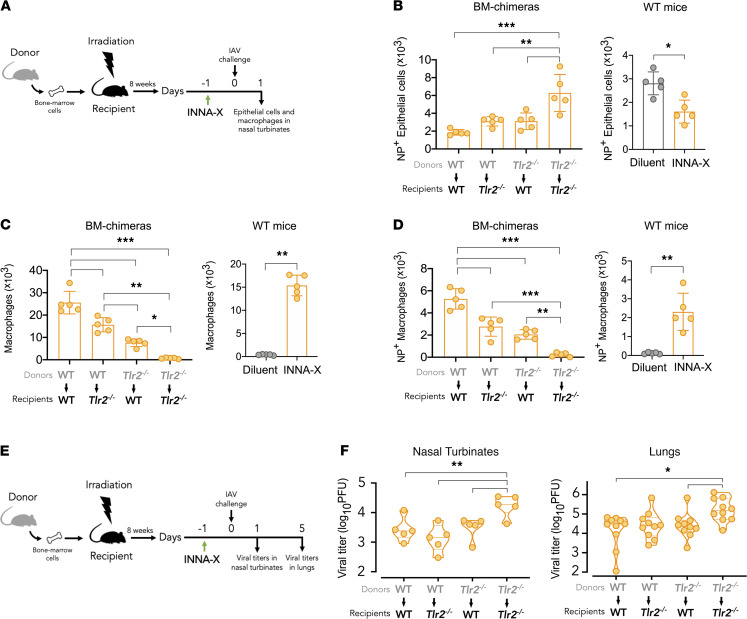
Figure 7. Contribution of immune and nonimmune cells in mediating protection.
(A) Bone marrow chimeras were established by adoptive transfer of donor bone marrow cells from WT C57BL/6 or Tlr2–/– mice into irradiated recipient mice (n = 5/group). After 8 weeks, animals were inoculated with 1 nmol of INNA-X prior to viral challenge with 500 PFU of Udorn IAV. Separate groups of WT mice were similarly treated with INNA-X and diluent prior to viral challenge. Nasal turbinates were harvested 1 day after challenge and the frequencies of (B) NP+-expressing CD45–CD31–EpCAM+ epithelial cells, (C) total macrophages, and (D) NP+-expressing macrophages determined. Results representative of 2 experiments conducted independently. (E and F) Viral titers in the nasal turbinates and lungs were also determined 1 and 5 days after infection, respectively. Statistical analysis of data from bone marrow chimeras (B–D and F) were performed by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test and data from WT mice analyzed by a Welch t test. Comparison of lung viral titers (F) analyzed by a Kruskal-Wallis multiple-comparison test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.