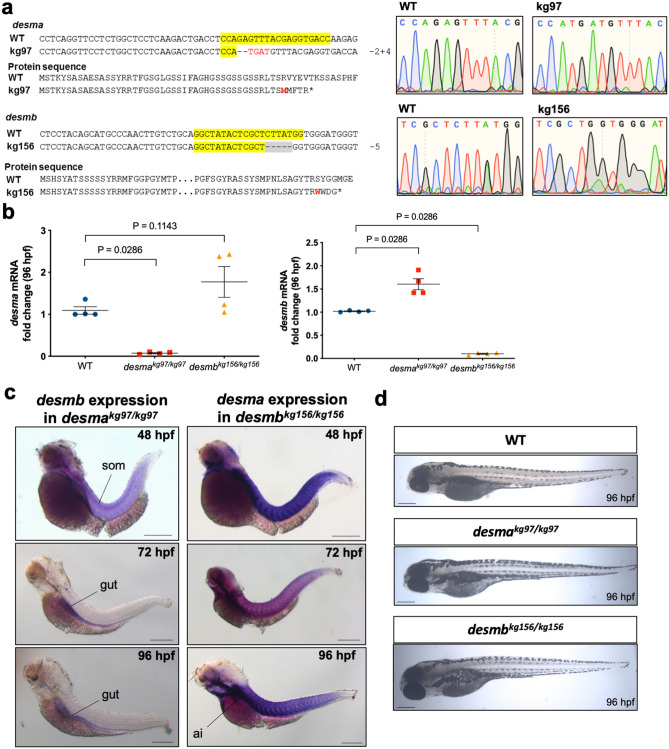
Figure 2.
Generation of desma and desmb knockout lines. (a) Alignments and chromatograms wild-type DNA sequences with mutant alleles, and predicted mutant polypeptide sequences. In DNA sequences, yellow highlights gRNA target sequence, hyphens show deleted bases, inserted bases are indicated in red font. In protein sequences, the first residue affected by the frameshift is indicated in red font, asterisks represent early stop codons. Chromatograms were created in SnapGene software (from Insightful Science; available at snapgene.com). (b) Quantitative real-time PCR results showing the expression of desma and desmb mRNA in wild-type and homozygous mutant 96 hpf embryos (N = 4, Mann–Whitney U). (c) Left panel shows whole mount in situ mRNA hybridisation of desmakg97 homozygous embryos at the indicated stages for antisense probes to desmb. Right panel shows whole mount in situ mRNA hybridisation of desmbkg156 homozygous embryos at the indicated stages for antisense probes to desma. Scale bar: 250 µm. Ai, anterior intestine; som, somite. (d) Brightfield pictures of 96 hpf WT and mutant embryos. Scale bar: 250 µm.