Fig. 3. Summary of identical and conserved amino acids from multiple sequence alignments.
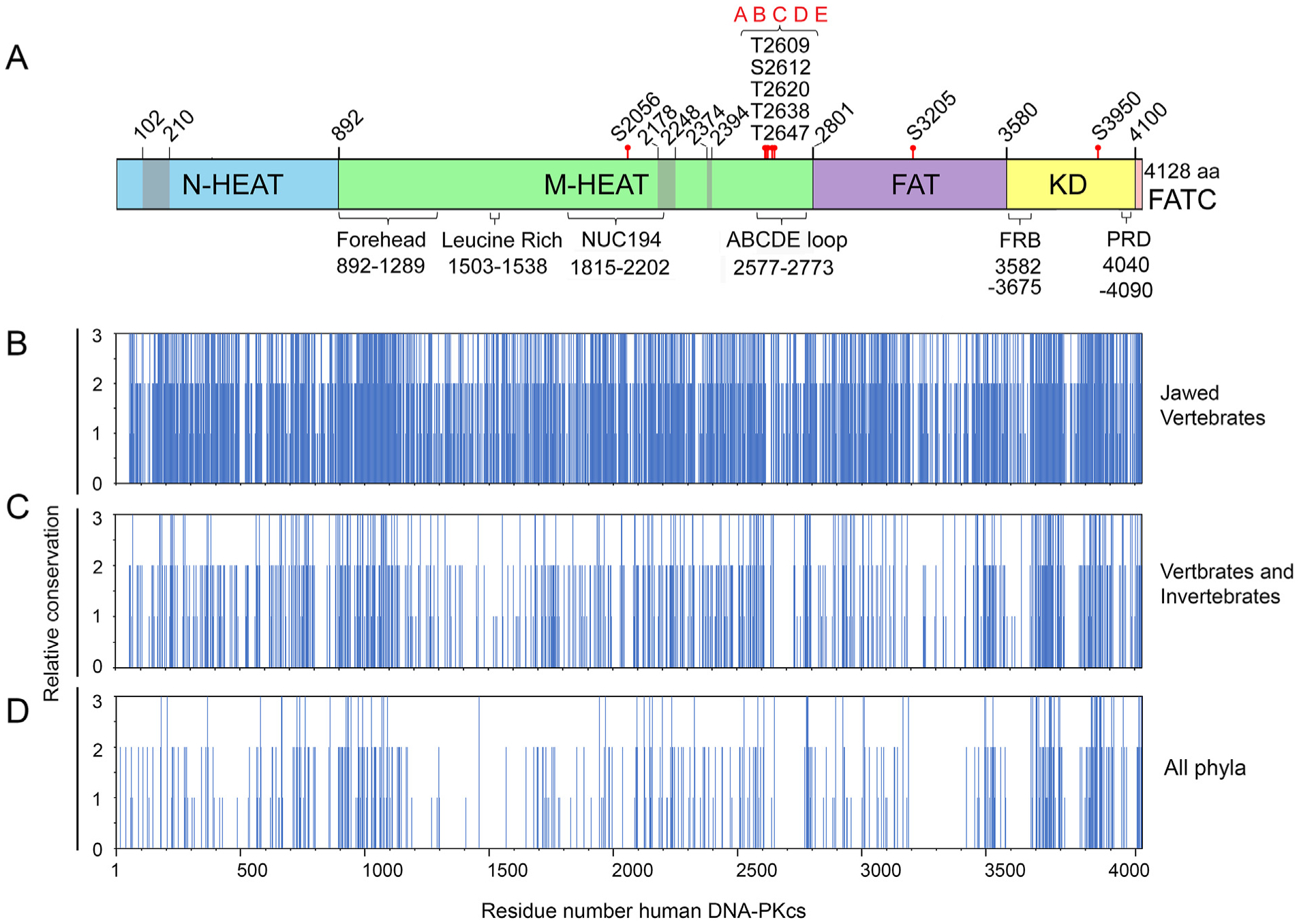
Panel A: Schematic of DNA-PKcs as in Fig. 1A showing location of the major domains and features. Panels B–D: Identical, conserved and semi-conserved amino acids from Clustal Omega alignments of (B) jawed vertebrates, (C) metazoa (vertebrates and invertebrates) and (D) representatives from all phyla. Complete alignments are shown in Suppl. Fig. 1, 2 and 4, respectively. The regions of amino acid identity and conservation from these alignments were plotted against amino acid number where 3 = amino acid identity (* in Clustal Omega alignments), 2 = amino acid conservation, (:) in Clustal Omega alignments and 3 = amino acid similarity (.) in Clustal Omega alignments.
