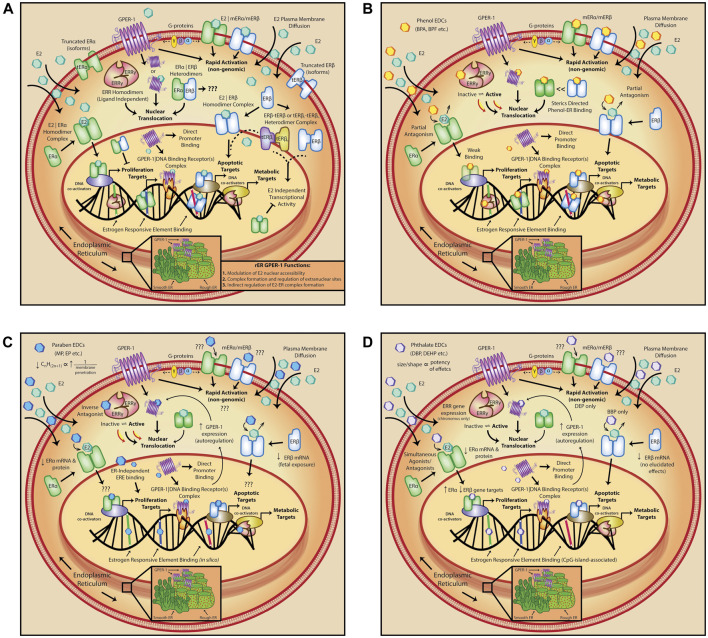
FIGURE 1.
Estrogen signaling and interference by varying categories of EDCs. (A) Diversity of estrogen signaling modalities; estradiol (E2) activates several receptor targets to transduce both genomic and non-genomic signaling pathways. (B) Phenol-induced deregulation impacts both estrogen receptors, (ER)α and ERβ by genomic/intracellular partial antagonism; binding of phenols is also sterically directed. (C) Paraben EDCs exhibit similar deregulation of estrogen signalling pathways, including decreased expression of both estrogen receptors, (ER)α and ERβ, but their activity is largely limited on the basis of alkyl-group size. (D) Phthalate compounds display simultaneous agonistic and antagonistic effects on estrogen signaling modalities; similar to parabens, phthalate effects are also size and shape dependent. E2, estradiol; ERR, estrogen related receptor; tER, truncated estrogen receptor; GPER-1, G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1; rER, rough endoplasmic reticulum; mER, membrane estrogen receptor; G-proteins, G-protein coupled receptor proteins; BPA, bisphenol A; BPF, bisphenol F; MP, methyl paraben; EP, ethyl paraben; BBP, benzyl butyl phthalate; DEP, diethyl phthalate; DEHP, di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate.