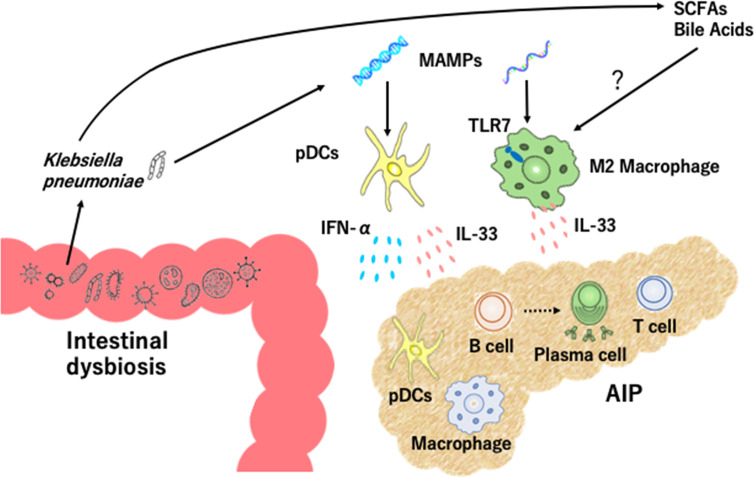
Figure 1.
Intestinal dysbiosis and autoimmune pancreatitis. Intestinal dysbiosis activates plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) which produce IFN-α and IL-33. Klebsiella pneumoniae and microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) activate pancreatic pDCs to produce IFN-α and IL-33. Recognition of MAMPs by toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) and exposure to short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and bile acids may lead to IL-33 production by M2 macrophages. Accumulation of pDCs and M2 macrophages in the pancreas causes infiltration of immune cells including IgG4-expressing plasmacytes, B cells, and T cells, destruction of acinar architecture, and fibrosis.