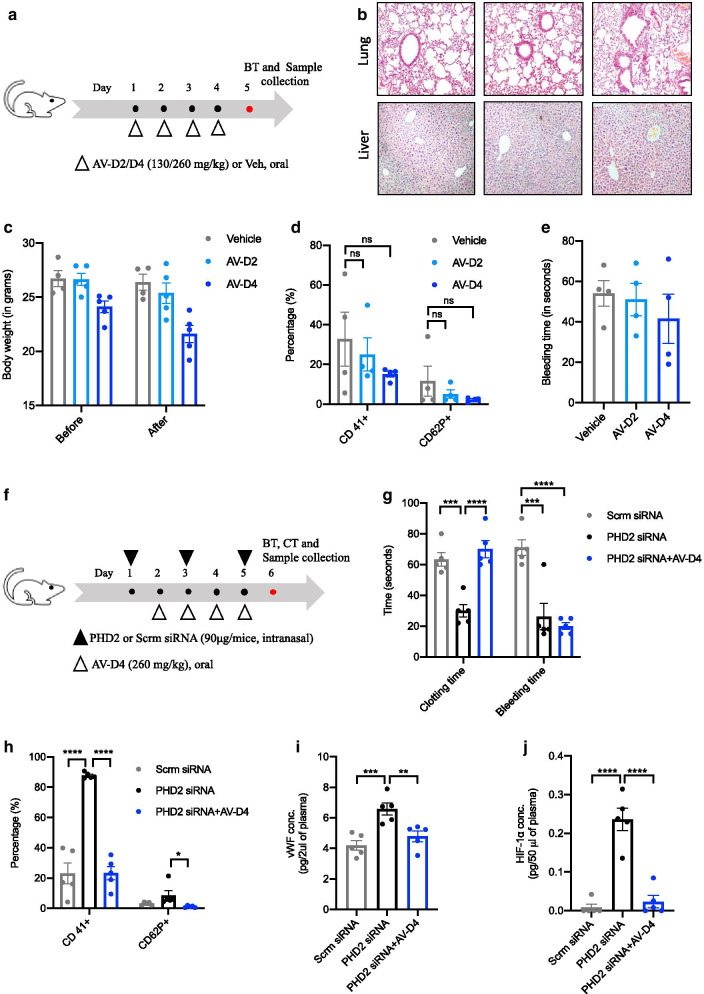
Fig. 2.
AV treatment to mice is protective against the blood coagulation phenotype in HIF-1α dependent manner. a Schematic representation of AV treatment protocol to naïve BALB/c mice. AV treatment was given for 4 consecutive days using AV-D2 (130 mg/kg) and AV-D4 dose (260 mg/kg). b Representative photomicrographs of fixed mouse lung and liver tissue sections stained with H&E (4× magnification) to asses AV mediated any effect on histological architecture in terms of inflammation. c Mice body weights measured before the start of the AV or Veh treatment and after the completion of treatment (AV or Veh) on day 5th of the protocol. d Total (CD41+) and active platelet (CD 62P+) count in mice whole blood (anticoagulated) measured by flow cytometry. e Tail bleeding time (in seconds) measured in Vehicle or AV treated mice as per the method described in the protocol. f Schematic representation of the siRNA experiment protocol. Scrambled or PHD2 siRNA was given intranasally to mice on days 1, 3, and 5. AV-D4 treatment was started therapeutically from day second and continued till 5h day of protocol as described in methods. On day six, mice were subjected to tail bleeding and clotting time assay. g Clotting and tail bleeding time (in seconds) measured in mice groups as described in methods. h Total (CD41+) and active platelet (CD 62P+) count assessed in mouse whole blood via flow cytometry. ELISA for estimation of i vWF and j HIF-1α levels in mouse plasma. Data are shown as mean ±SEM of four to five mice per group. Term ns represents the non-significant. Significance denoted by *P≤0.05, **P≤0.01, ***P≤0.001 and ****P≤0.0001 and determined by ordinary one way ANOVA) using GraphPad