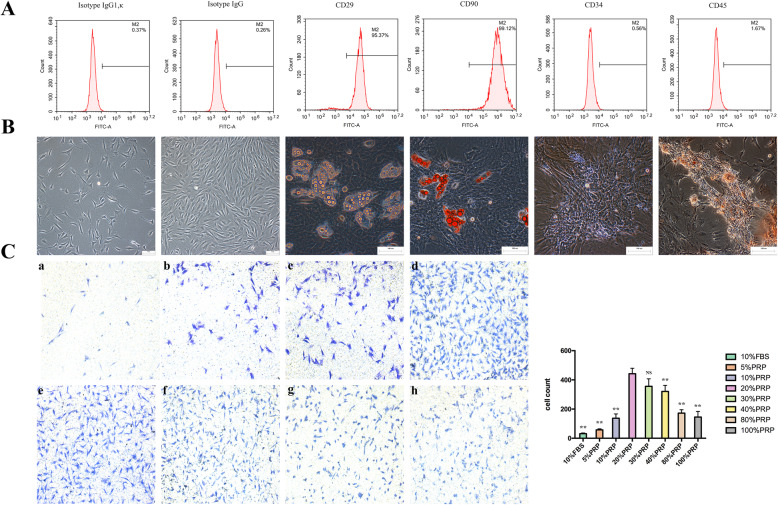
Fig. 2.
Characterization of ADSCs and the optimal concentration of PRP for combination with ADSCs. a Immunophenotypical analysis of ADSCs by flow cytometry. Passage 3 ADSCs, which were positive for CD29 and CD99 and negative for CD34, expressed typical MSC surface antigens. b Multipotent differentiation properties of ADSCs. Passage 3 ADSCs were cultured in adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation media for 21 days. Then, differentiation was evaluated by staining lipid droplets with oil red O (adipogenic, right), and calcium nodules were detected by Alizarin red staining (osteogenic, left). Representative images of 3 independent experiments are shown. Scale bars = 100 μm. c Migration efficiency was evaluated by crystal violet staining and microscopy and quantified with ImageJ. The analysis generally suggested that the optimal concentration of PRP in combination with ADSCs was 20%, with efficiencies ranging from 5 to 100%. All experiments were performed in triplicate and were repeated three times to confirm the findings (*p < 0.05). One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post hoc test showed statistically significant differences overall between the eight groups. Values were expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5 high-powered fields per well, three wells per group). Significance was set to *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001