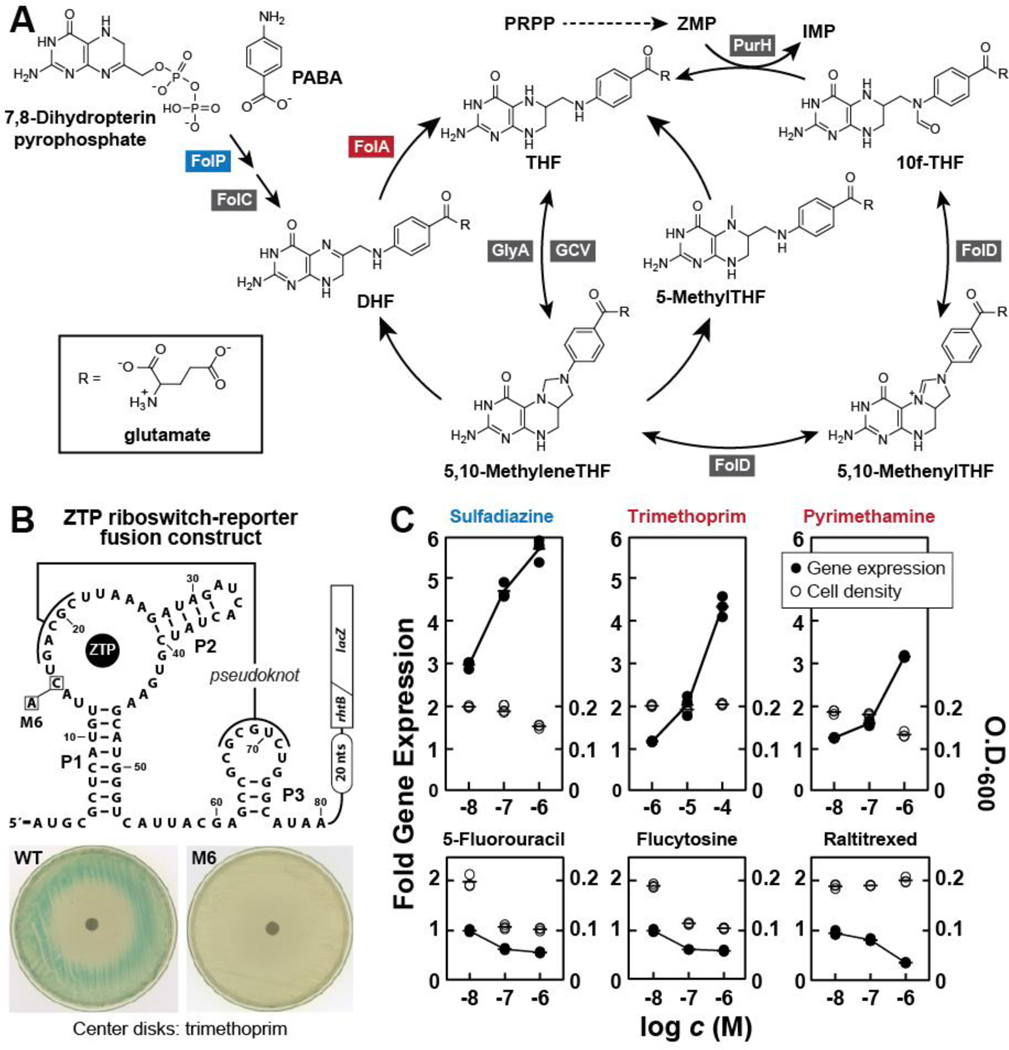
Figure 2. The Folate Pathway is Inhibited by Antifolates that Trigger ZTP Riboswitch-Mediated Gene Expression.
(A) Schematic representation of the metabolites of folate biosynthesis and recycling in E. coli. Enzymes listed (boxed and named for their genes) are those whose inhibition might trigger ZTP riboswitch-mediated reporter gene activation by causing a reduction in 10f-THF concentration, and a subsequent increase in ZTP concentration. Note that FolA (red, dihydrofolate reductase) is inhibited by various antibiotics such as trimethoprim and methotrexate, and FolP (blue, dihydropteroate synthase) is inhibited by sulfonamide-based antibiotics such as sulfadiazine.
(B) The design and function of a ZTP riboswitch-reporter fusion construct. (Top) Sequence and secondary structure model for a ZTP riboswitch aptamer derived from the rhtB gene of the bacterial species Pectobacterium carotovorum, depicted fused to a β-galactosidase reporter gene from E. coli as adapted from the construct created previously (Kim et al., 2015). The gene control mechanism of this riboswitch is presumed to operate by regulating ribosome access to the ribosome binding site (Shine-Dalgarno sequence). A mutant version of the ribowitch carrying a single C15A change (M6) that is known (Kim et al., 2015) to prevent ZTP binding and thus cannot activate gene expression was also used in this study. (Bottom) Agar diffusion assays depicting the effects of the addition of 10 μL of a 10 mM solution of trimethoprim (TMP) on filter disks. Plates are uniformly innoculated with E. coli cells carrying the wild-type (WT) or mutant (M6) reporter construct in LB media containing x-gal.
(C) Plots of the relative levels of reporter gene expression (β-galactosidase activity levels, left y-axis, filled circles) and bacterial cell density (O.D.600, right y-axis, open circles) versus the logarithm of the concentration (c) of various test compounds (x-axis) when tested in M9 minimal media. Gene expression values are normalized to cells grown in culture media without test compound added. Top row depicts data gathered for known antifolates (sulfadiazine, trimethoprim, and pyrimethamine) expected to affect ZTP levels. The antifolate compound names are colored to reflect their enzyme targets depicted in A. Bottom row depicts similar data for other drug compounds (5-fluorouracil, flucytosine, raltitrexed) that are believed to target certain folate-dependent enzymes whose inhibition is not expected to affect ZTP levels.