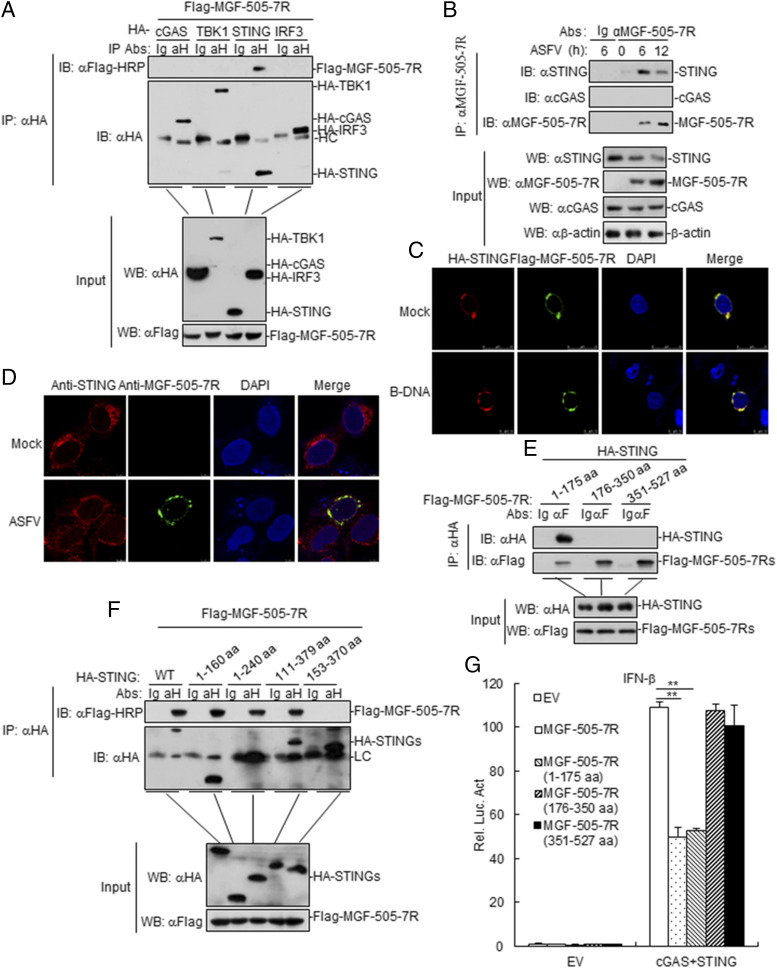
FIGURE 5.
ASFV MGF-505-7R interacts with STING. (A) MGF-505-7R interacted with STING but not with cGAS, TBK1, and IRF3 in the overexpression system. 293T cells (2 × 106) were transfected with the indicated plasmids (5 μg each). Coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analyses were performed with the indicated Abs. The expression of transfected proteins was analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-HA or anti-Flag Abs. (B) Endogenous associations between MGF-505-7R and STING. PAM cells were left infected or infected with ASFV for the indicated times before coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis. (C) Colocalization of MGF-505-7R with STING. HeLa cells were transfected with HA-STING (1 μg) and Flag-MGF-505-7R (1 μg) plasmids. Twenty hours after transfection, cells were retransfected with B-DNA (1 μg/ml) for 12 h before confocal microscopy. (D) Confocal microscopy of Ma-104 cells infected with ASFV for 8 h. (E and F) Domain mapping of MGF-505-7R and STING interaction. 293T cells were transfected with the indicated truncation plasmids before coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis with the indicated Abs. HA-STINGs: HA-STING, HA-STING (1–160 aa), HA-STING (1–240 aa), HA-STING (111–379 aa), and HA-STING (153–370 aa). (G) Effects of ASFV MGF-505-7R or its mutants overexpression on cGAS-STING–triggered IFN-β promoter activation. 293T cells (1 × 105) were transfected with IFN-β reporter (0.1 μg) and MGF-505-7R or MGF-505-7R’s mutants expression (0.1 μg) plasmids for 24 h before luciferase assays were performed. All the experiments were repeated three times with similar results. Data are shown as means ± SD; n = 3. **p < 0.01. EV, empty vector; αH, anti-HA; HC, H chain; Luc, luciferase; WT, wild-type.