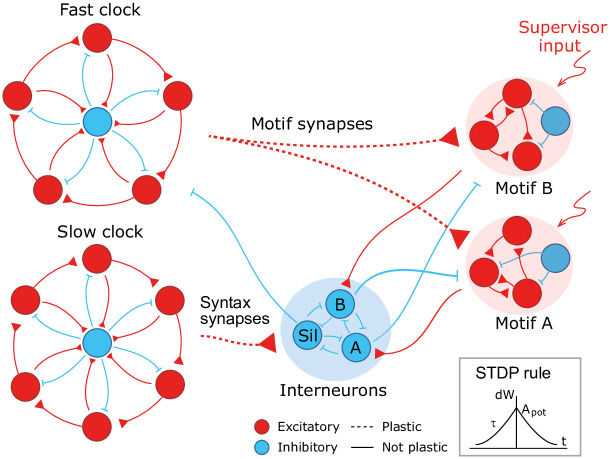
Fig 1. A cartoon of the model.
Dynamics in the read-out networks (A and B) is learnt and controlled on two time scales. The fast time scale network (fast clock) exhibits sequential dynamics that spans individual motifs. This acts directly on the read-out networks through plastic synapses. These synapses learn the motifs. The slow time scale network (slow clock) exhibits sequential dynamics that spans the entire sequence of motifs. This acts indirectly on the read-out networks through an interneuron network. The synapses from the slow clock to the interneurons are plastic and learn the right order of the motifs, or the syntax. The plastic synapses follow a simple symmetric STDP rule for potentiation, with a constant depression independent of spike time.