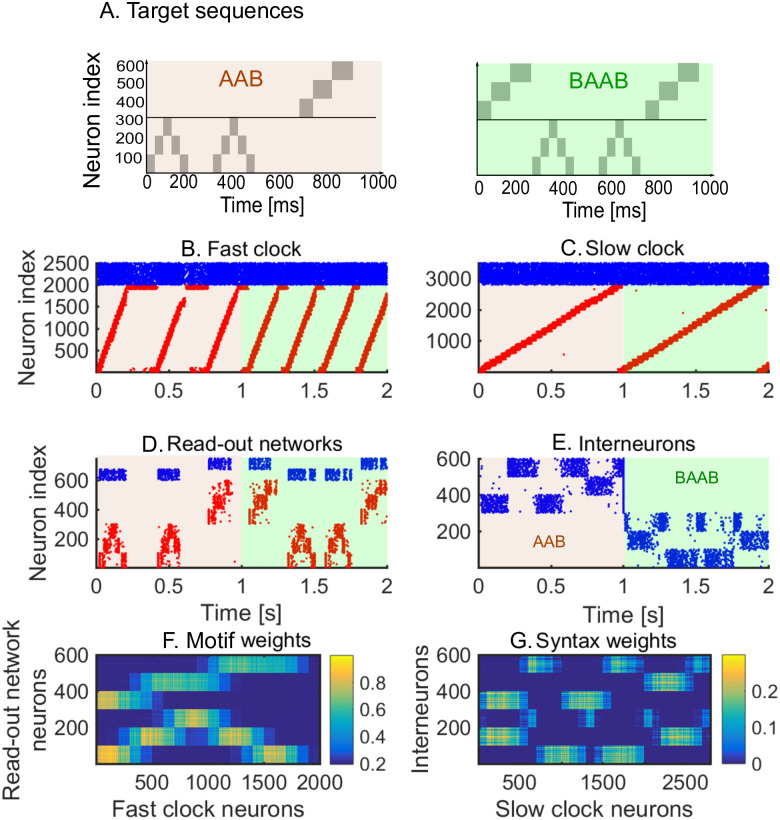
Fig 6. Spontaneous dynamics after learning two sequences alternately (80 learning iterations).
A. The target sequences. B-E. Red dots: excitatory neurons; blue dots: inhibitory neurons. Brown shaded area: sequence AAB is played by inhibiting the interneurons related to the second sequence; light green shaded area: sequence BAAB is played by inhibiting the interneurons related to the first sequence. B. Spike raster of the fast clock. C. Spike raster of the slow clock. D. Spike raster of the two read-out networks. E. Spike raster of the interneurons. An external attentional inhibitory current selects which sequence is played. F. The motif weights encode the two motifs. Note the similarity with Fig 2F: the same motifs are re-used in both sequences. G. The syntax weights encode the two motif orderings. Note the difference with Fig 2G: an additional syntax is stored. All motif and syntax synapses are plastic at all times during the sequence presentations.