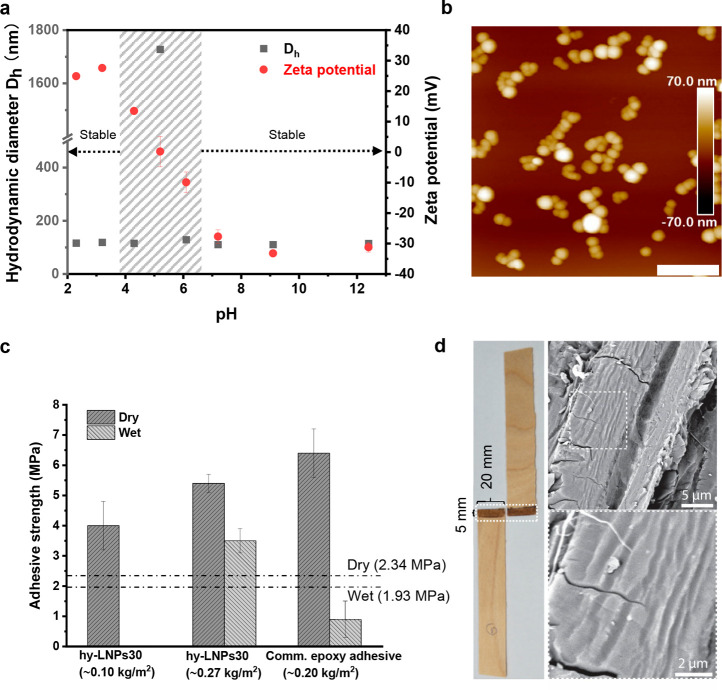
Figure 5.
Application demonstration of the hy-LNPs: Covalent cationization of the cured hy-LNPs20 and the adhesive use of the uncured hy-LNPs30 for wood. (a) Average hydrodynamic diameter (Dh) and ζ potential of the cationized cured hy-LNPs20 plotted against pH. The shaded area marks the surface charge transition of the cationized particles. (b) AFM height image shows the particle morphology of the cationized particles obtained at pH 2.3 (scale bar: 400 nm). (c) Adhesive strength of the hy-LNPs30-based waterborne adhesive (41 wt % solid content) and a commercial epoxy adhesive from Loctite for birch veneers (11.5 × 2 × 0.15 cm3). Mean ± standard error of three replica are shown. The dashed lines denote the minimum dry/wet adhesive strength requirements for the urea-formaldehyde-type adhesive according to ASTM-D4690. (d) Photographic profile and SEM images of the glued area (20 × 5 mm2) after adhesive test.