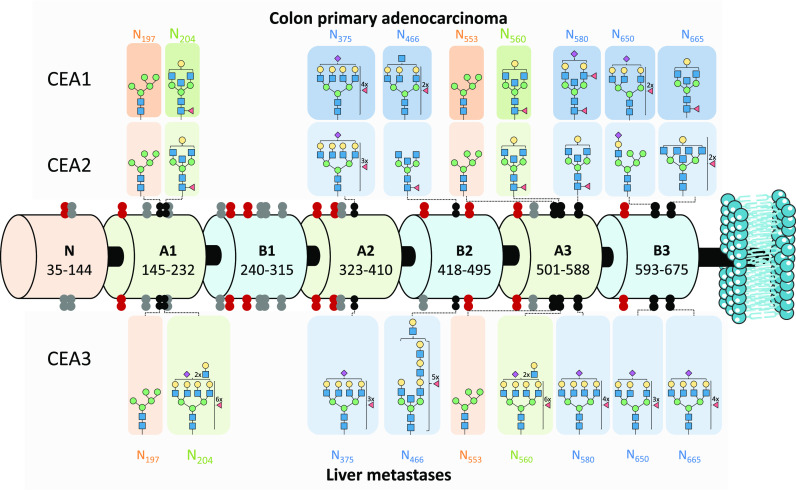
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEACAM5_HUMAN) domain structure with the N-glycosylation sites revealed by this study marked for the different type of CEA samples. The CEA domains are depicted as barrels and N-glycosylation sites (shown as double dots) are mapped along the structure. The black double dots are identified N-glycosylation sites in this study (tryptic or Glu-C digest) and are supplied with the most abundant N-glycan composition per all three types of CEA analyzed (side panels). The N-glycans highlighted in orange (N197 and N553) and in green (N204 and N560) share the same peptide backbone, hence the discovered glycan populations are shared. Confidently characterized by nonspecific digestion data sites are shown as red double dots (Pronase) and are not accompanied by the most abundant glycan structures due to the lack of reliable quantification. Undiscovered N-glycosylation sites are shown as gray double dots. All identified N-glycopeptides can be found in Supporting Information, Table S2 (quantified) and S3 (nonquantified)). Blue square: N-acetylglucosamine (N), green circle: mannose (H), yellow circle: galactose (H), red triangle: fucose (F), pink diamond: N-acetylneuraminic acid (S).