Figure 2.
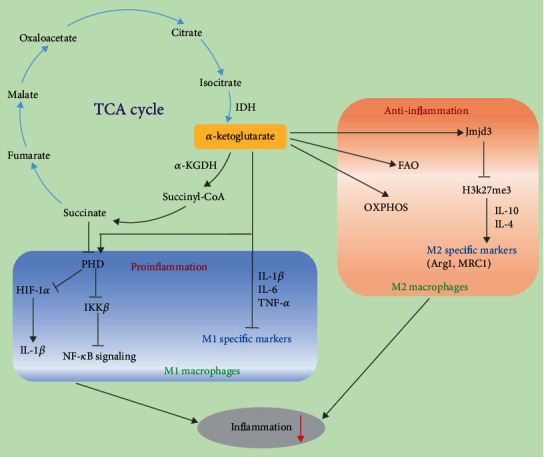
The regulatory mechanism of α-ketoglutarate on M1 and M2 polarization. In M1 macrophages, α-ketoglutarate inhibits M1 polarization by enhancing PHD activity to suppress IKKβ activation and the NF-κB pathway and inhibiting HIF-1α and IL-1β expression mediated downstream of succinate in the TCA cycle. In M2 macrophages, α-ketoglutarate generated by glutaminolysis is a checkpoint that regulates M2 metabolic reprogramming and the participation of FAO and OXPHOS in M2 macrophages. Additionally, α-ketoglutarate promotes M2 activation through the α-ketoglutarate-Jmjd3 pathway by suppressing H3K27me3 and increasing the expression of M2-specific markers.
