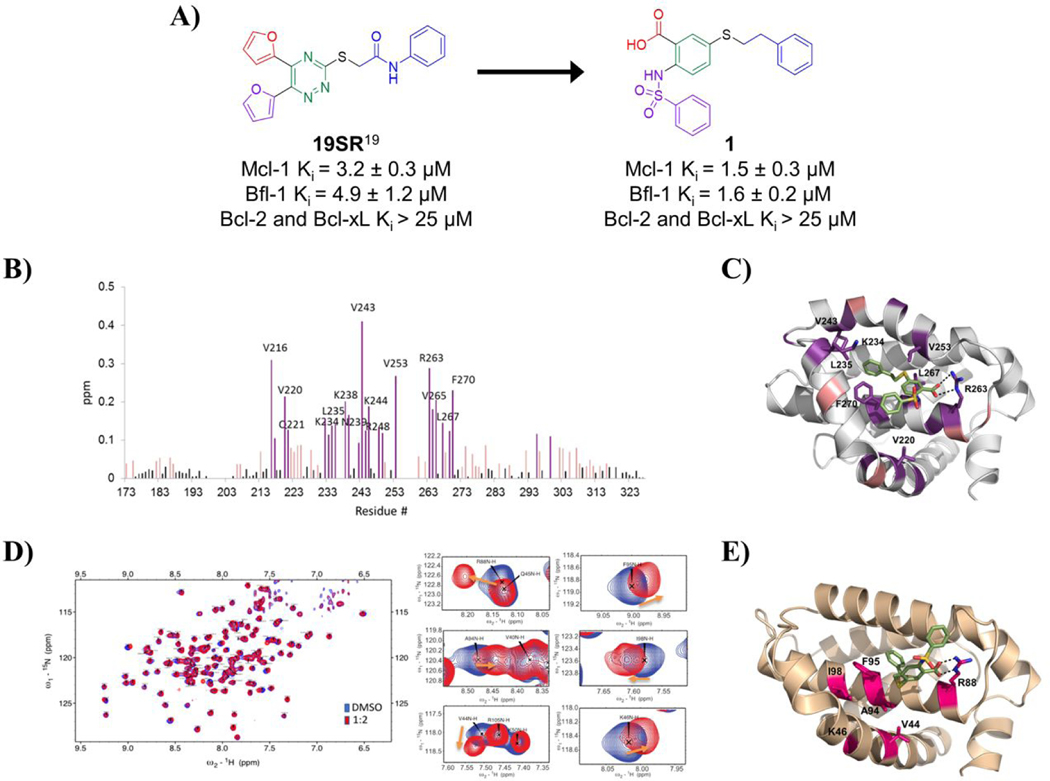
Figure. 1. Design of compound 1 and its binding site characterization to Mcl-1 and Bfl-1 with HSQC-NMR spectroscopy and computational docking.
A) Chemical structures and binding affinity of compounds 19SR19 and 1, against Bcl-2 family anti-apoptotic proteins (distinct structural features color coded). B) HSQC-NMR chemical shift perturbations of Mcl-1 residues in the presence of 1. C) Predicted binding pose of 1 in the BH3 binding site of Mcl-1 (PDB ID: 4HW2 was used for docking); key residue shifts highlighted corresponding to shift intensity noted in HSQC-NMR experiments. D) Superimposed 15N-HSQC spectra of Bfl-1 in the absence (blue) and presence (red) of compound 1 with close up view of select residue shifts. E) Predicted binding pose of 1 to Bfl-1 (PDB ID: 3MQP used for docking) with highlighted residues shifted in HSQC-NMR spectra.