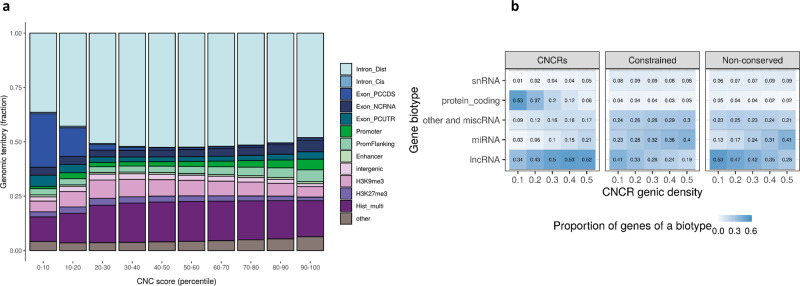
Fig. 2. Genomic territory and biotype proportions of constrained, non-conserved regions.
Composition of the constrained genome, partitioned by constrained, non-conserved (CNC) scores (a) and proportion of biotypes of genes in our annotation (constrained, non-conserved regions: CNCRs) and in the comparator annotations (constrained regions and non-conserved regions) (b). The description for each genomic feature is shown in Supplementary Table 1. The barplot in a shows the genomic features for the 12.5% most constrained regions with CNC scores partitioned by decile, such that the highest decile (90–100) represents the most constrained and least conserved regions. Description of gene biotypes in b is taken from Ensembl42. The heatmap demonstrates the proportion of genes of a certain biotype within the three separate annotations within each genic CNCR density cut-off. CNCR density is defined as the proportion of CNCRs within a gene taking into account the gene size. Protein coding is defined by a gene that contains an open reading frame. The subclassified components of long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) found in the annotations are: Antisense—has transcripts that overlap the genomic span (i.e. exon or introns) of a protein-coding locus on the opposite strand; lincRNA (long interspersed ncRNA)—has transcripts that are long intergenic non-coding RNA locus with a length > 200 bp; non-coding RNA is further subclassified into miRNA (microRNA); siRNA (small interfering RNA); snRNA (small nuclear RNA) and miscellaneous RNA (includes snoRNA (small nucleolar RNA) and tRNA (transfer RNA)). Pseudogenes are similar to known proteins but contain a frameshift and/or stop codon(s) which disrupts the open reading frame. These can be classified into processed pseudogene—a pseudogene that lacks introns and is thought to arise from reverse transcription of mRNA followed by reinsertion of DNA into the genome and unprocessed pseudogene—a pseudogene that can contain introns since produced by gene duplication.