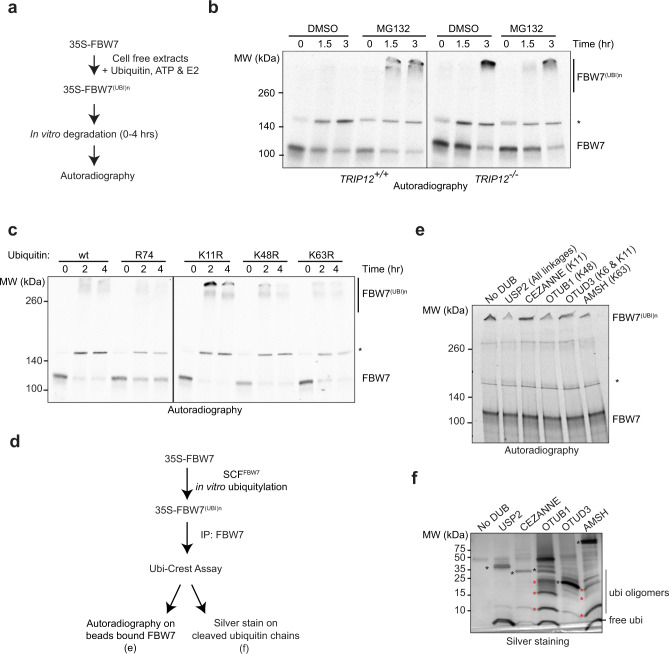
Fig. 6. TRIP12-mediated K11-linked ubiquitylation is essential for FBW7 proteasomal degradation.
a Schematic of in vitro degradation assay. b In vitro 35S-FBW7α degradation assay performed in cell-free extracts from cells of the indicated genotypes and visualised by autoradiography. c In vitro FBW7 degradation assay performed in cell-free extracts in the presence of the indicated ubiquitin mutants and visualised by autoradiography. d Schematic for in vitro ubiquitylation and ubiquitin restriction enzyme digest experiment for 35S-FBW7. e Autoradiographs showing cleavage of beads-bound polyubiquitylated 35S-FBW7 by the indicated DUBs. Linkage specificity is given in parentheses. Black stars (*) in b, c, and e represent the nonspecific band of unknown identity. f Silver stain on cleaved ubiquitins in the supernatant from the experiment in e, black stars represent respective DUBs and red stars label uncleaved ubiquitin oligomers. All blots are representative of at least three independent experiments with the exception of e, which was done twice with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.