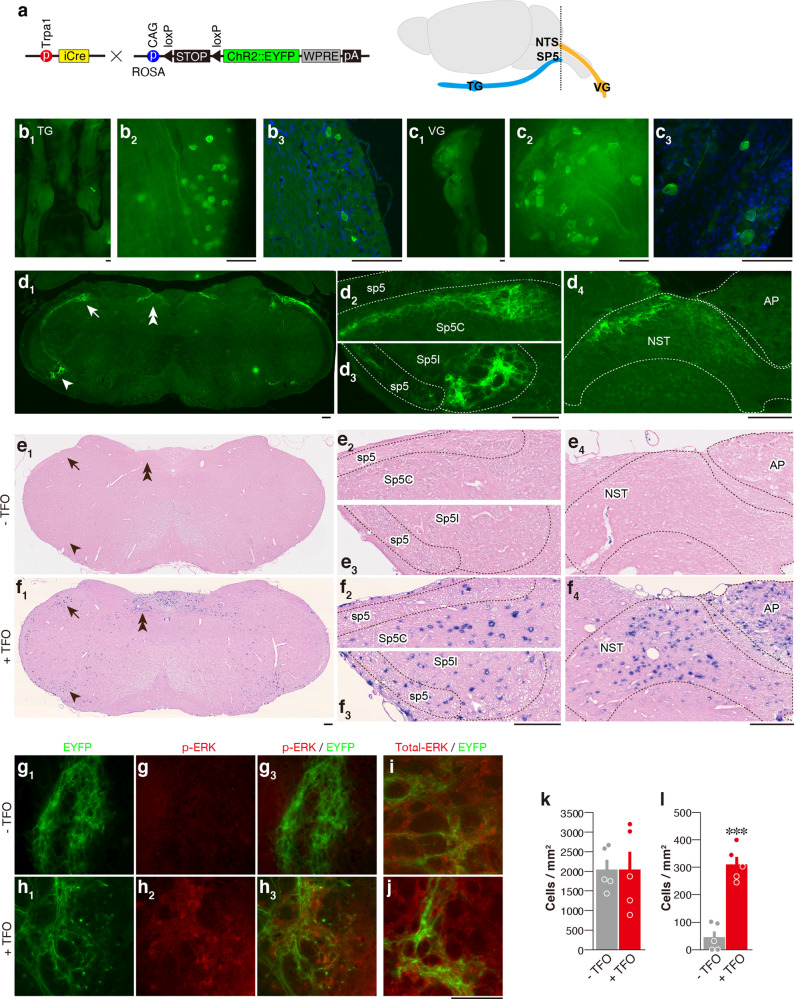
Fig. 4. Projection sites of Trpa1+ neurons in the Sp5/NTS.
a Strategy for selective labeling of Trpa1+ cells using Trpa1-Cre and RCL-ChR2/EYFP mice. Schematic illustration of trigeminal and vagus nerve projections to the brainstem are also shown. A dotted line indicates the approximate position of the sections shown in d−j. b−d Representative EYFP signals in the TG (b1−b3), VG (c1−c3), and medulla (d1) of whole mount views (b1, c1), magnified whole-mount views (b2, c2), and tissue sections (b3, c3, d1) of Trpa1-Cre; RCL-ChR2/EYFP double transgenic mice. Enlarged images of Sp5C (d2; area indicated by arrow in d1), Sp5I (d3; area indicated by arrowhead in d1), and NTS (d4; area indicated by double arrow in d1) are also shown. In the Sp5I/C transition area, YFP-positive fibers were observed in the dorsal (arrow) area in the Sp5C and ventral area in the Sp5I (arrowhead) regions (d1). e1−f4 Representative images of in situ hybridization of c-fos RNA in the medulla following IP injection of saline (e1−e4) and tFO (4E2MT; f1–f4), along with enlarged images of the Sp5 (e2, e3, f2, and f3) and NTS (e4, f4). g−l Expression of phospho-ERK and total ERK was compared with EYFP signals in the ventral EYFP-fiber-rich area in the Sp5 after IP injection of saline (g, i) and tFO (4E2MT; h, j). Quantification of total ERK (k; n = 5 for each, p = 0.9984) and pERK (l; n = 5 for each, p < 0.0001) are also shown. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test was used to assess significance. Scale bars, 100 µm; ***p < 0.001.