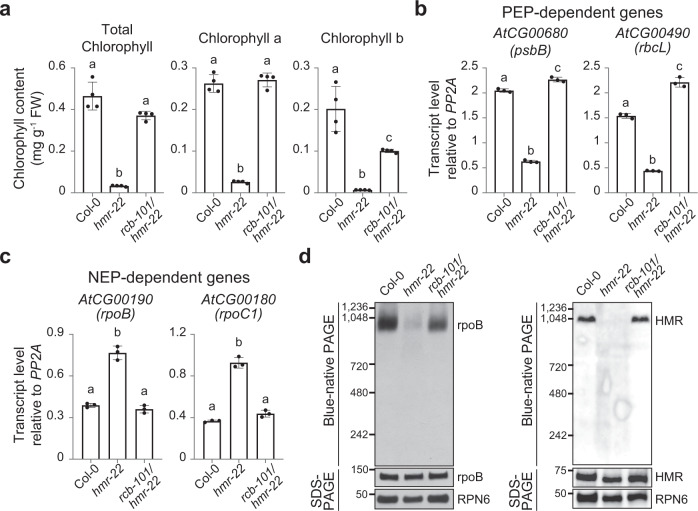
Fig. 4. rcb-101 rescues hmr-22′s defects in chloroplast biogenesis.
a Quantification of total chlorophyll, chlorophyll a, and chlorophyll b in 4-d-old Col-0, hmr-22, and rcb-101/hmr-22 seedlings grown in 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light at 21 °C. b, c qRT-PCR analyses of two PEP-dependent genes, psbB and rbcL (b), and two NEP-dependent genes, rpoB and ropC1 (c), in 4-d-old Col-0, hmr-22, and rcb-101/hmr-22 seedlings grown in 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light at 21 °C. Transcript levels were calculated relative to those of PP2A. For a, b, c, error bars represent the s.d. of three (b, c) or four (a) biological replicates. The centers of the error bars represent the mean values. Different letters denote statistically significant differences between the samples (ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD, p < 0.01, n = 3 or 4 biological replicates). d Immunoblots showing the level of the PEP complex (blue-native PAGE) and the levels of rpoB (left panel) or HMR (right panel) (SDS-PAGE) in 4-d-old Col-0, hmr-22, and rcb-101/hmr-22 seedlings grown in 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light at 21 °C. RPN6 was used as a loading control. The immunoblot experiments were independently repeated at least three times, and the results of one representative experiment are shown. The source data of the chlorophyll measurements in (a), the qRT-PCR data in (b, c), and the immunoblots in (d) are provided in the Source Data file.