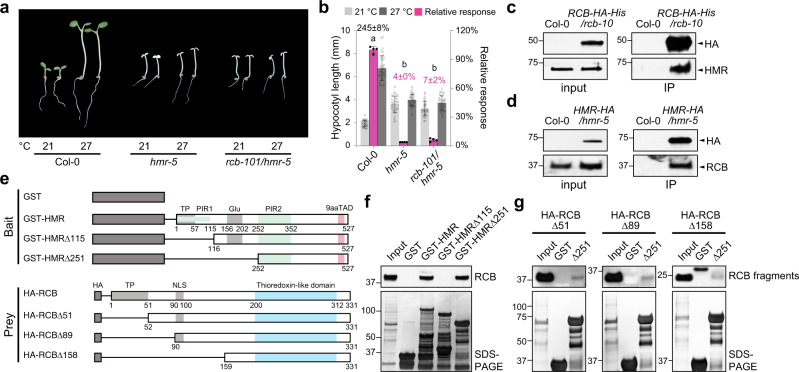
Fig. 6. RCB directly interacts with HMR.
a Representative images of 4-d-old Col-0, hmr-5, and rcb-101/hmr-5 seedlings grown in 50 μmol m−2 s−1 R light in either 21 or 27 °C. b Hypocotyl length measurements of the seedlings shown in (a). The percent increase in hypocotyl length (mean ± s.d., n = 4 biological replicates) of Col-0 in 27 °C is shown in black above its columns. The magenta bars show the relative response. Error bars for the hypocotyl measurements represent s.d. (n > 30 seedlings); error bars for the relative responses represent the s.d. of four biological replicates. The centers of the error bars represent the mean values. Purple numbers show the mean ± s.d. values of relative responses and different letters denote statistically significant differences in relative responses (ANOVA, Tukey’s HSD, p < 0.01, n = 4 biological replicates). c, d Reciprocal co-immunoprecipitation experiments showing the interaction between RCB and HMR in vivo. c Immunoblots showing the co-immunoprecipitation results using 4-d-old RCB-HA-His/rcb-10 seedlings grown in 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light. RCB-HA-His was pulled-down using Pierce™ anti-HA agarose. RCB-HA-His and HMR from the input and pulldown fractions were detected by immunoblots using anti-HA and anti-HMR antibodies, respectively. d Immunoblots showing the co-immunoprecipitation results using 4-d-old HMR-HA/hmr-5 seedlings grown in 10 μmol m−2 s−1 R light. HMR-HA was pulled-down using Pierce™ anti-HA agarose. HMR-HA and RCB from the input and pulldown fractions were detected by immunoblots using anti-HA and anti-RCB antibodies, respectively. For (c, d), samples from Col-0 seedlings grown in the same conditions were used as negative controls. e Schematics of the bait and prey proteins used in the GST pulldown assays to show a direct interaction between HMR and RCB. TP: transit peptide; Glu: Glu-rich region; PIR2: PHYA-interacting region 2; 9aaTAD: 9-amino-acid TAD (amino acids 512-520). f GST pulldown assays using GST-tagged full-length or N-terminal truncations to pulldown in vitro translated HA-tagged full-length RCB (HA-RCB). g GST pulldown assays using GST-tagged HMR∆251 (∆251) to pulldown in vitro translated HA-tagged N-terminal RCB truncations. For (f, g), the upper panels are immunoblots using anti-HA antibodies showing the bound and input fractions of either HA-tagged full-length RCB (f) or the various RCB truncation fragments (g); the lower panels are Coomassie Blue-stained SDS-PAGE gels showing immobilized GST and GST-tagged HMR and HMR fragments. The pulldown experiments in (c, d, f, g), were independently repeated two times, and the results of one representative experiment are shown. The source data of the hypocotyl measurements in (b) and the immunoblots in (c, d, f, g) are provided in the Source Data file.