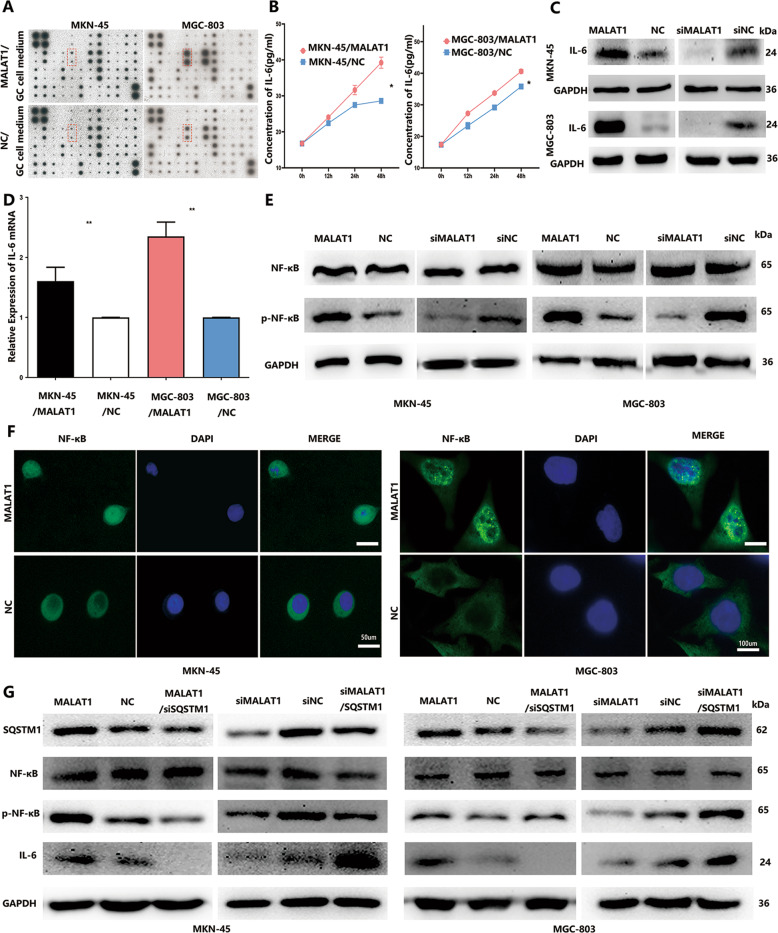
Fig. 4. Blockage of autophagy induced IL-6 secretion via SQSTM1/NF-κB pathway activation.
A Human cytokine antibody arrays were used to screen the difference of conditioned medium between GC cells transfected with MALAT1 overexpression vectors and NC vectors; B IL-6 protein expression level in the MKN-45/MALAT1, MGC-803/MALAT1, and compared groups was quantified 24 h after changing the culture medium as measured by ELISA (MKN-45/MALAT1 vs MKN-45/NC: 39.24 ± 1.24 vs 28.62 ± 0.17; MGC-803/MALAT1 vs MGC-803/NC: 40.6 ± 0.47 vs 35.79 ± 0.08, P < 0.05); C, D The mRNA and protein levels of p-IL-6 were detected in MKN-45 and MGC-803 cells transfected with MALAT1 overexpression vectors. Silencing MALAT1 resulted in IL-6 protein level downregulation (MKN-45/MALAT1 vs MKN-45/NC: 1.61 ± 0.2 vs 1 ± 0.07; MGC-803/MALAT1 vs MGC-803/NC: 2.35 ± 0.2 vs 1 ± 0.07, P < 0.01); E The NF-κB and p-NF-κB protein levels were increased in MKN-45 and MGC-803 cells transfected with MALAT1 overexpression vectors. Silencing MALAT1 resulted in p-NF-κB level reduction; F MKN-45 and MGC-803 cells were transfected with MALAT1 overexpression vectors, and the NF-κB subcellular locations were determined by immunofluorescence assay; G P-NF-κB and IL-6 expressions were abrogated in MKN-45/MALAT1 and MGC-803/MALAT1 cells with SQSTM1 siRNA treatment. Transfected SQSTM1 plasmid into MKN-45 and MGC-803 cells reversed NF-κB/IL-6 pathway inactivation caused by MALAT1 siRNAs. Three biological replicates were performed for in vitro assays. Bars, S.D.; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.