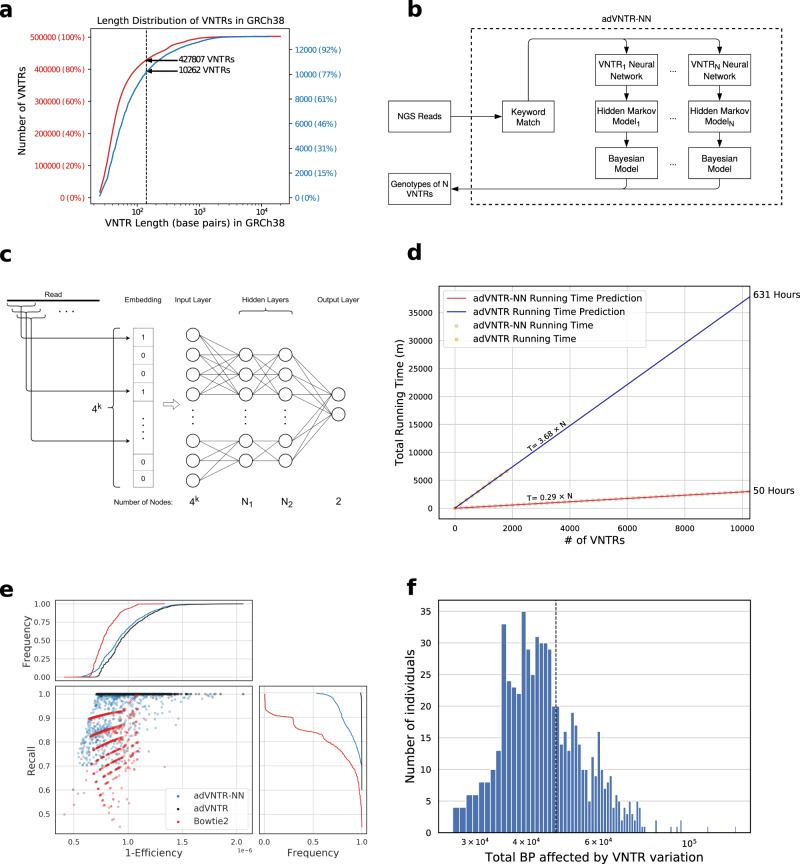
Fig. 1. VNTR performance.
a Length distribution of all known VNTRs (red) and selected targeted VNTRs (blue) across the GRCh38 human genome in base pairs. b The genotyping pipeline. c Neural network architecture for each VNTR which uses a mapping of reads to a k-mer composition vector. d Improvement in running time after using neural network and k-mer matching. e Accuracy and efficiency of read recruitment in simulated data. The scatter plot shows 1-efficiency ((TP + FP)/R) and recall (TP/(TP + FN)) of classification with different methods. High efficiency is related directly with running time. Each of 10,264 points represents a VNTR locus (Method) and are shown once for each method. The side and top panels show cumulative distributions of recall and 1-efficiency. f Base pairs (log-scale) affected by VNTRs per individual in the GTEx cohort. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.