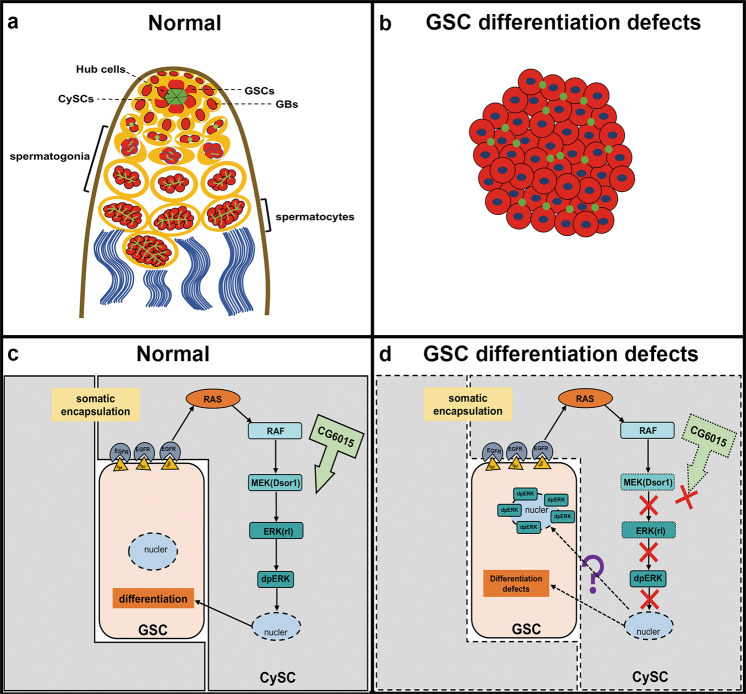
Fig. 8. Schematic representation of CG6015 and EGFR signaling in the Drosophila testis.
a, b Graphical representation of the apical tips of normal testes and testes with GSC differentiation defects. c, d Mechanisms of CG6015 and EGFR signaling. In normal testes, the stem cell niche is composed of GSCs, CySCs, and hub cells, which occupy the apical tips of the testis. For the integrity of germ cell differentiation, somatic cells should envelop germ cells, and fusomes gradually transition from dot to bifurcate. Somatic inactivation of CG6015 and key targets in the EGFR signaling pathway lead to the accumulation of undifferentiated germ cells, and eventually the formation of tumor-like germ cell cysts with pointed fusomes in the Drosophila testis. Our results show the maintenance of stem cell niche homeostasis by CG6015 and EGFR signaling via germline dpERK signals.