FIG. 6.
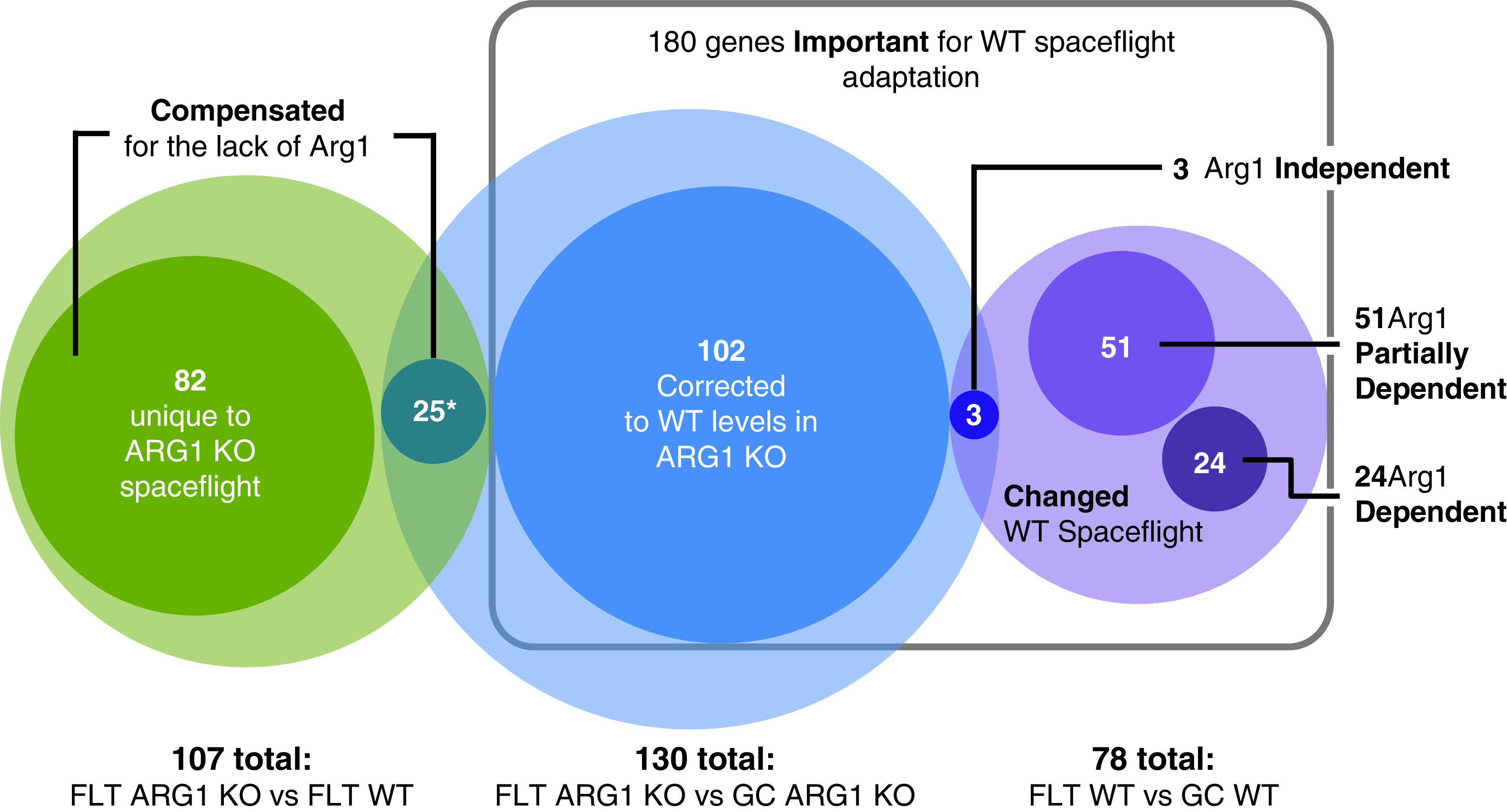
The gene landscape for physiological adaptation to spaceflight. At least 180 genes are Important for spaceflight adaptation. These genes were not differentially expressed in the spaceflight transcriptomes between WT and ARG1 KO. Seventy-eight genes in WT and 130 in ARG1 KO were differentially expressed in the physiological adaptation to spaceflight, thus also between spaceflight and ground. Three of these genes were coordinately expressed in both genotypes; thus they were independent of Arg1 function. Of the 78 genes of the WT physiological adaptation to spaceflight, 51 were at least partially dependent, and 24 were dependent on Arg1. There were 102 genes whose expression needed to be corrected to WT spaceflight adaptation levels in the ARG1 KO cells. There were 107 genes that were differentially expressed in the spaceflight transcriptomes between ARG1 KO cells in spaceflight and WT cells in spaceflight; 25 of these genes compensated for the lack of a functional Arg1 gene in the ARG1 KO cells and were part of the physiological adaptation to spaceflight ARG1 KO cells alone (Fig. 4A Category IV and Fig. 4B, Category I indicated with *), 82 of these genes compensated for the lack of a functional Arg1 gene in the ARG1 KO cells but were not a part of the physiological adaptation to spaceflight.
