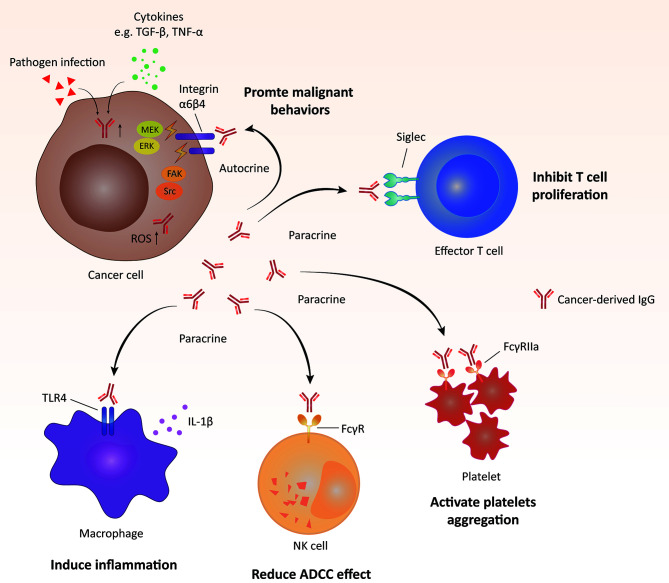
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of action of cancer-derived IgG. Cancer-derived IgG promotes tumorigenesis in autocrine and paracrine manners.(i) Cancer-derived IgG interacts with integrins located on the tumor cell membrane and then activates downstream pathways, including FAK/Src, MEK/ERK/c-Myc and reactive oxygen species (ROS) pathways. (ii) Cancer-derived IgG interacts with different membrane receptors of other types of cells, including Siglec of T cells, Toll-like receptor (TLR) of macrophages and FcγR of natural killer (NK) cells and platelets, and further regulates the functions of these cell types. ADCC, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity.