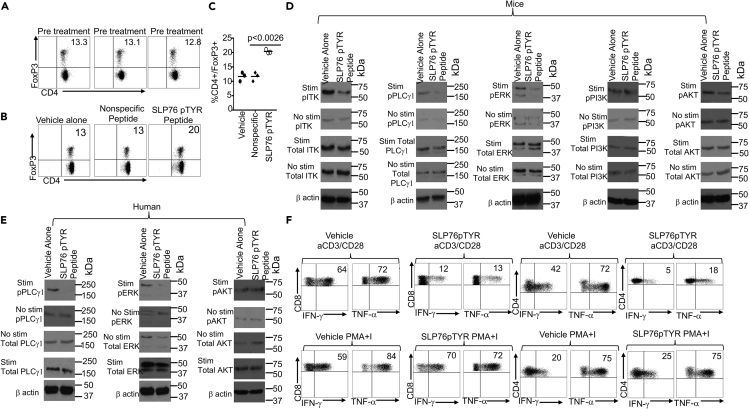
Figure 6.
Novel peptide SLP76pTYR specifically targets SLP76:ITK signaling and enhances Treg cell development
(A) Murine CD4+ T cells were examine for total CD4+ and FOXP3 expression prior to treatment with SLP76pTYR. n = 3, and one representative experiment is shown.
(B) Total T cells stimulated in the presence of SLP76pTYR, nonspecific peptide, or vehicle alone were examined for total CD4 cells that are FoxP3+. n = 3, and one representative experiment is shown.
(C) Quantification of three experiments as in (A).
(D) Cell lysates were obtained from mouse T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of SLP76pTYR, or vehicle alone. Lysate from stimulated cells and non-stimulated cells were examined for phosphorylated ITK, total ITK (size 50–75kDa), phosphorylated PLCγ1, total PLCγ1 (size ~155kDa), phosphorylated ERK, total ERK (size ~42kDa), phosphorylated PI3K, total PI3K, (size ~85kDa), phosphorylated AKT, and total AKT (size ~60kDa). n = 3 and one representative experiment is shown.
(E) Cell lysates from human T cells, non-stimulated or stimulated with OKT3 for 5min in the presence of SLP76pTYR or vehicle alone, were examined for phosphorylated pPLCγ1 and total PLCγ1 on stimulated and non-stimulated T cells. Cell lysate from stimulated and non-stimulated cells were examine for pERK and total ERK. Lysates from stimulated and non-stimulated were also examined for phosphorylation and total AKT. n = 3 and one representative experiment is shown.
(F) Primary human T cells from PBMCs were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28, or with PMA/Ionomycin, for 6 hr in the presence of vehicle alone or SLP76pTYR in the presence of Brefeldin A (BFA) (Webb et al., 2015). Intracellular IFN-γ and TNF-α expression by CD8+ and CD4+ T cells was determined by flow cytometry. For statistical analysis we used two-way ANOVA and Student's t test. p values are presented. See also Figure S8.