Fig. 1.
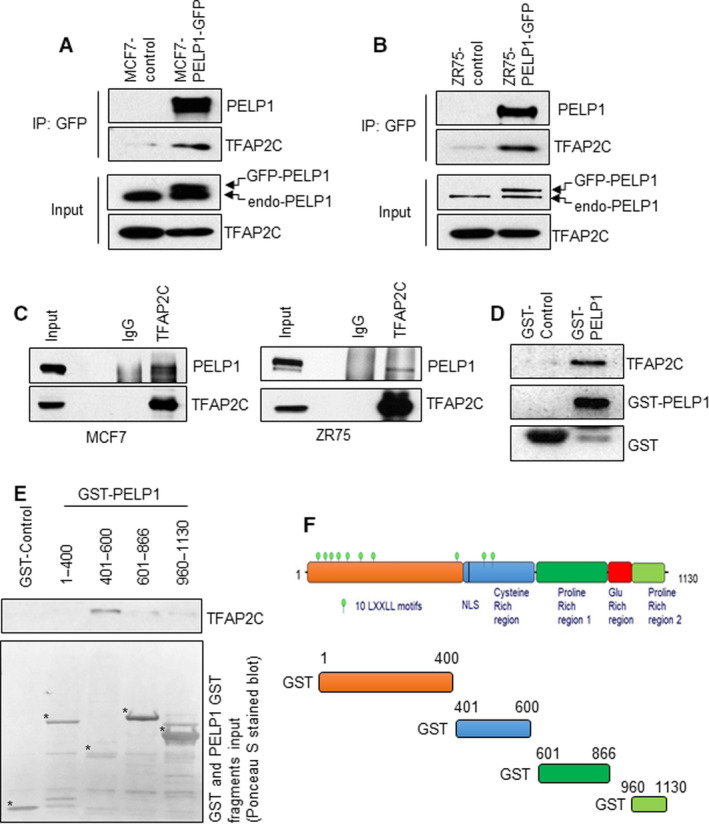
PELP1 interacts with TFAP2C. (A, B) Total lysates from MCF7‐control and MCF7‐GFP‐PELP1 cells (A) or ZR75‐control and ZR75‐GFP‐PELP1 cells (B) were subjected to IP using the GFP‐TRAP beads, and the TFAP2C interaction was verified by western blotting (n = 2). (C) Total lysates from MCF7 and ZR75 cells were subjected to IP using the control IgG or TFAP2C antibody, and the PELP1 interaction was verified by western blotting (n = 2). (D) Total lysates from MCF7 cells were subjected to GST pull‐down assays using the purified control GST or GST‐PELP1 full‐length proteins expressed in Escherichia coli and the TFAP2C interaction was verified by western blotting. (E) Escherichia coli expressed and purified GST‐PELP1 deletions were used to identify TFAP2C interacting regions in the PELP1 protein using MCF7 total lysates. (F) Schematic representation of GST‐PELP1 deletions utilized in the pull‐down assays.
