Fig. 5.
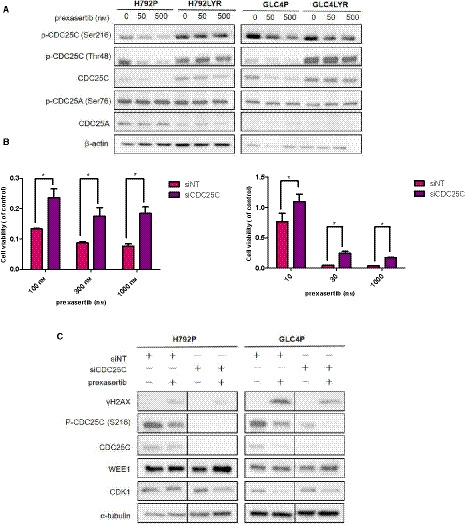
Inactivation of CDC25C contributes to the resistance to Chk1 inhibition. (A) CDC25 homolog family protein expression in H792 and GLC4 parental and resistant cells. The cells were exposed to indicated concentrations of prexasertib for 48 h and WB was performed. (B) Cell viabilities for GLC4P and H792P cells by CellTiter‐Glo. Cells were transfected with small interfering (si)CDC25C for 24 h to knock down CDC25C expression and then exposed to different concentrations of prexasertib for 72 h. *P < 0.05. (C) Expression of CDC25C and other proteins as indicated in H792P and GLC4P cells by WB. Alpha‐tubulin was used as a loading control. Cells were transfected with siCDC25C for 24 h, then exposed to prexasertib 50 nm for 48 h. All data for cell viability test are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Unpaired and two‐tailed Student’s t‐test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ns, not significant.
