Fig. 8.
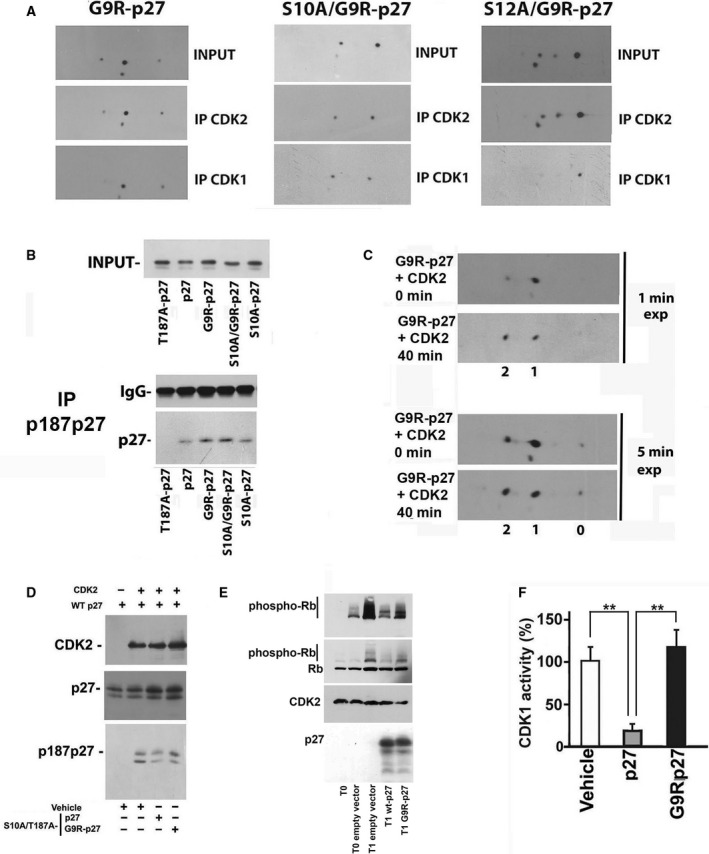
Effect of G9R‐p27 on CDK activities and putative identification of G9R‐p27 S12 kinases. (A) PC‐3 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.0 plasmids encoding G9R‐p27, S10A/G9R‐p27, and S12A/G9R‐p27. The nuclear compartments were purified and immunoprecipitated with rabbit pAb against CDK1 and CDK2. Each set of IPs was analyzed by 2D/WB, together with input extract. From left to right, 2D/WB analyses for G9R‐p27, S10A/G9R‐p27, and S12A/G9R‐p27 transfected cells are shown. Further details are reported under ‘Materials and methods’. (B) PC‐3 cells were transfected with pcDNA3.0 plasmids encoding T187A/p27, p27, G9R‐p27, S10A/G9R‐p27, and S10A‐p27. After 24‐h transfection, cells were treated with Mg132 (a proteasome inhibitor) for additional 8 h. Subsequently, nuclear extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti‐p187p27 rabbit pAb. The IP was then analyzed by western blotting employing anti‐p27 mAb. Extract from T187A/p27‐expressing cells was used to confirm the specificity of anti‐p187p27 pAb. On the top, input extracts were evaluated. On the bottom, the IP materials were tested for IgG and p27 content. Further details are reported under Materials and methods. (C) G9R‐p27 protein was prepared from PC‐3‐transfected cells. The partially purified protein was incubated with active human recombinant CDK2/CycE‐GST enzyme. Then, the assay mixtures at time zero and after 40 min of incubation were analyzed by 2D/WB. The films were exposed for different time periods to support the conclusions reached in the text. Further details are reported under Materials and methods. (D) Partially purified dephosphorylated human WT‐p27 was incubated with active human recombinant CDK2/CycE‐GST enzyme in the presence of IVTT S10A/T187A‐p27 or S10A/T187A‐G9R‐p27, to compare the inhibition activity of these latter proteins. The abrogation of the phosphorylatable site in T187 and in S10 (S10A/T187A mutants) was introduced to avoid the recognition of these sites as substrate in the in vitro assay of CDK2. Vehicle represents product of IVTT reaction carried in the presence of empty vector. Anti‐p187p27 rabbit pAb was used to evaluate CDK2 activity on human recombinant WT‐p27 protein. Anti‐p27 and anti‐CDK2 antibodies were used as controls of the experiment. (E) CDK2 assay determination was performed employing human recombinant active CyclinE/CDK2 and Rb as substrate. The first lane from left (T0, zero time) corresponds to a control assay, that is, a mixture including CyclinE/CDK2 and Rb but not incubated at 30 °C. T0 empty vector (second lane) is a control assay (i.e., a not incubated assay) that includes CyclinE/CDK2, Rb and a PC‐3 cell extract transfected with a pcDNA3.0 empty vector. All T1 lanes correspond to assay reactions incubated for 1 h at 30 °C. In particular: T1 empty vector mixture includes Rb, CyclinE/CDK2, and PC‐3 cell extract transfected with a pcDNA3.0 empty vector; T1 wt‐p27 includes Rb, CyclinE/CDK2, and PC‐3 cell extract transfected with a vector encoding wt‐p27, and T1 G9R‐p27 includes Rb, CyclinE/CDK2, and PC‐3 cell extract transfected with a vector encoding G9R‐p27. Additional details are reported under Materials and methods. The assay reactions were analyzed by 1D/WB employing antibodies against phospho‐Rb, Rb, CDK2, and p27. (F) CDK1 assay determination was performed employing ADP‐Glo Kinase Assay Kit and human recombinant active CDK1/Cyclin A2. The reaction mixtures included (or did not include, Vehicle) partially purified wt‐p27 or G9R‐p27. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean of three independent experiments. Data were analyzed by Student's t‐test. **P < 0.01.
