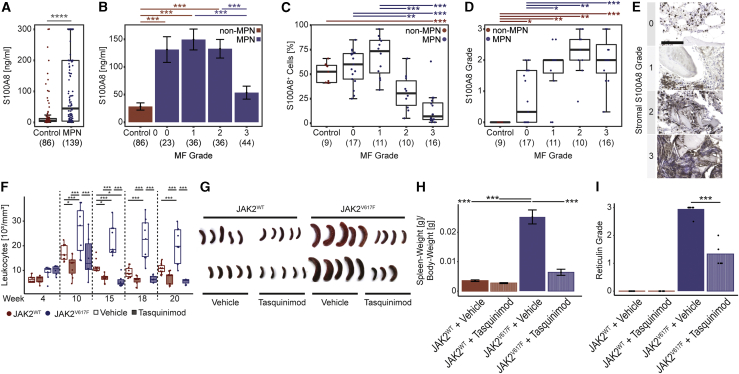
Figure 7.
Spatial kinetics of S100A8/S100A9 detects disease progression in MPN and their pharmacological targeting ameliorates the disease
(A) ELISA of S100A8 (and S100A9) in MPN (blue) and controls (red) plasma. Two-tailed, two-sample Welch test was used.
(B) ELISA of S100A8 (and S100A9) in MPN with different MF grades (blue) and controls (red) plasma. Mean ± SEM. One-way-ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s was used.
(C) Frequency of S100A8+ cells BM biopsies; n = 64 patients. One-way-ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s HSD was used.
(D and E) Grading of S100A8 in the non-hematopoietic compartment in BM biopsies. Scale bar, 100 μm. n = 64 patients. Kruskal-Wallis H test with post hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used. p values were adjusted for multiple hypothesis testing by the Holm-Bonferroni method.
(F) White blood cell counts of WT mice transplanted with either JAK2V617F (blue) or JAK2WT overexpressing HSPCs (red) each either treated with Tasquinimod 30 mg/kg/day or vehicle control. Two-way repeated ANOVA pairwise comparisons were analyzed by estimated marginal means.
(G) Spleens at sacrifice as indicated.
(H) Relative spleen weights. Mean ± SEM. One-way-ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s HSD.
(I) Reticulin (MF) grade. Kruskal-Wallis H test with post hoc Wilcoxon rank-sum test.
See also Figure S6.