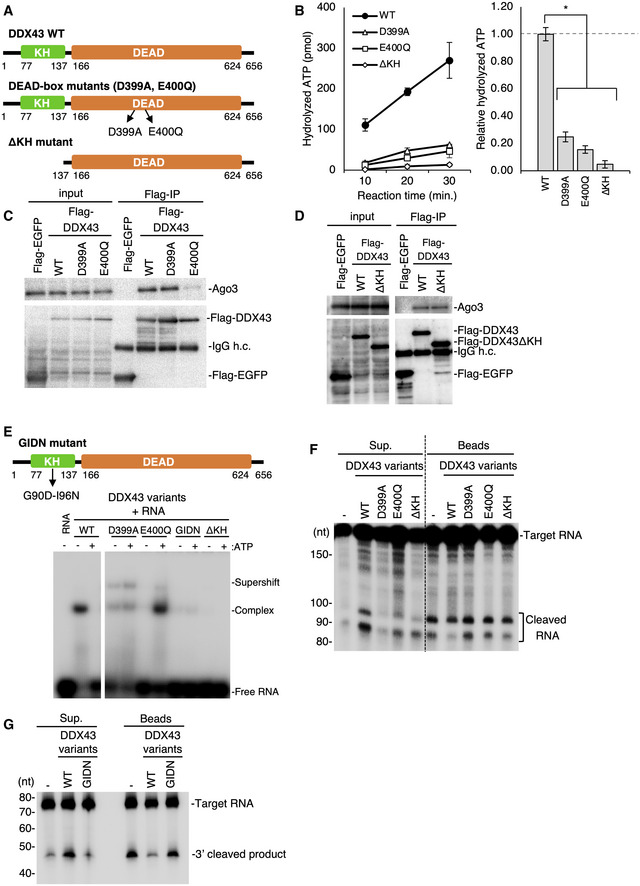
The domain organization of DDX43 and detail of the mutants. The conserved KH domain and DEAD‐box helicase domain are indicated. D399 and E400 are highly conserved residues within the ATPase active site in the helicase domain.
Quantification of ATPase activity of DDX43 variants. The graph on the right indicates the ratio of the hydrolyzed ATP produced by DDX43 mutants to that of the WT DDX43. Data represent the mean ± standard deviations. n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.002 as determined with the t‐test.
Immunoprecipitation of Ago3 with Flag‐tagged DDX43 WT and its D399A and E400Q mutants. Ago3 and DDX43 were detected by Western blotting using anti‐Ago3 and anti‐Flag‐antibodies, respectively. Flag‐EGFP was used as a negative control. The E400Q mutation in DDX43 impairs the interaction between Ago3 and DDX43. IgG h.c.: IgG heavy chain.
Immunoprecipitation of Ago3 with Flag‐tagged DDX43 WT and its ΔKH mutant lacking KH domain. Ago3 and DDX43 were detected by Western blotting using anti‐Ago3 and anti‐Flag‐antibodies, respectively. Flag‐EGFP was used as a negative control. The ΔKH mutant maintains affinity to Ago3. IgG h.c.: IgG heavy chain.
RNA‐binding activity of DDX43 variants as analyzed by EMSA. Upper: The GIDN mutant was substituted G90 and I96 conserved within the KH domain to Asp and Asn, respectively. Lower: A 40‐nt single‐stranded RNA was 5′ end‐labeled with 32P and incubated with DDX43 variants in the presence or absence of 0.1 mM ATP. Supershift means non‐canonical complex.
RNA‐unwinding assays upon Ago3‐piRISC‐dependent target RNA cleavage. Unwinding activities of DDX43 WT and its D399A, E400Q, and ΔKH mutants are shown. RNAs cleaved by Ago3 are shown as “Cleaved RNA”.
RNA‐unwinding assays upon Ago3‐piRISC‐dependent target RNA cleavage. Unwinding activities of DDX43 WT and its GIDN mutant are shown. RNA cleaved by Ago3 is shown as “3′ cleaved RNA”.