Figure 6.
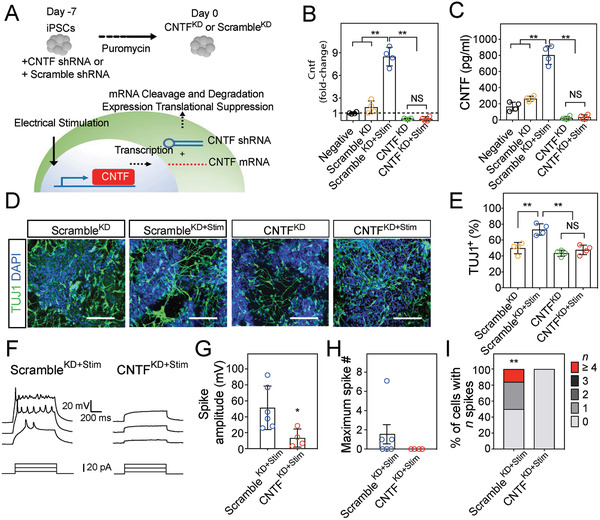
Neuronal conversion of iPSCs on soft CGSStim was attenuated with Cntf gene knockdown. A) Schematic demonstrating shRNA blocking CNTF mRNA expression. B) qRT‐PCR analysis of Cntf. C) CNTF in the supernatants of samples was determined by ELISA. D) Immunocytofluorescence analysis of TUJ1+ (green) cells on soft CGS with or without an exposure to the stimulation. Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars indicate 100 µm. E) Quantification of TUJ1+ cells cultured on soft CGS. iPSCs modified by CNTFKD with electrical stimulation (CNTFKD+Stim) did not show a statistical significant difference compared to CNTFKD (without an exposure to the stimulation). F) Representative traces of membrane potentials of iPSC‐derived cells on soft CGSStim with the control scrambled knockdown (ScrambleKD+Stim, left) and CNTF knockdown (CNTFKD+Stim, right). G) The summary result of averaged spike amplitude of ScrambleKD+Stim and CNTFKD+Stim conditions. H,I) Maximum spike number and quantification of percentage of cells with indicated firing frequencies at 14d of differentiation on soft CGS with electrical stimulation. CNTFKD was tested and ScrambleKD was utilized as a control group. B,C,E) Analyzed using a one‐way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's HSD post hoc test with ** p < 0.01. NS indicates no‐significance between CNTKKD and CNTFKD+Stim (p > 0.99, p = 0.99, and p = 0.77, respectively). Values represent the mean of independent experiments (n = 4); error bars, SD. G,H) Analyzed using a paired Student's t‐test with * p < 0.05, respectively. N = 6 and 4 for ScrambleKD+Stim and CNTFKD+Stim, respectively from four batches of independent cell cultures.
