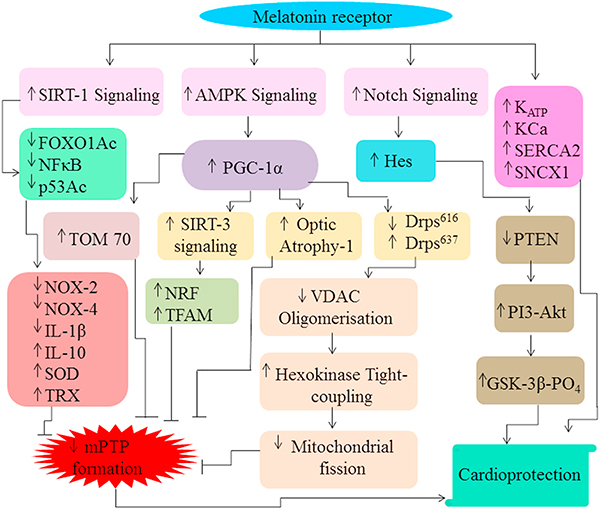
Fig. 2.
Activation of MTR enhances SIRT-1 signaling which subsequently deacetylases FOXO1, P53 and decreases NFκB activity. This eventually results in reduction in the expression of NOX-2, NOX-4, IL-1β but augmentation in IL-10, SOD, TRX activity. Also, melatonin boosts AMPK signaling which results in an increase in the level of PGC-1α. PGC-1α further modulates the expression of TOM70, optic atrophy-1, Drps637, Drps616 and increases SIRT-3 signaling which ultimately reduce MPTP formation. Increased SIRT-3 signaling increases the expression of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 and mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) to abate MPTP opening. Moreover, the alteration in the level of Drps637, Drps616 expression reduces VDAC1 oligomerization, disassociation of hexokinase 2 to reduce mitochondrial fission which leads to MPTP formation. Apart from this, increased Notch signaling up-regulates Hes which further decreases phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) levels. PTEN further increases PI3/Akt signaling to escalate GSK-β (glycogen synthase kinase-3) phosphorylation to induce cardioprotective effects.