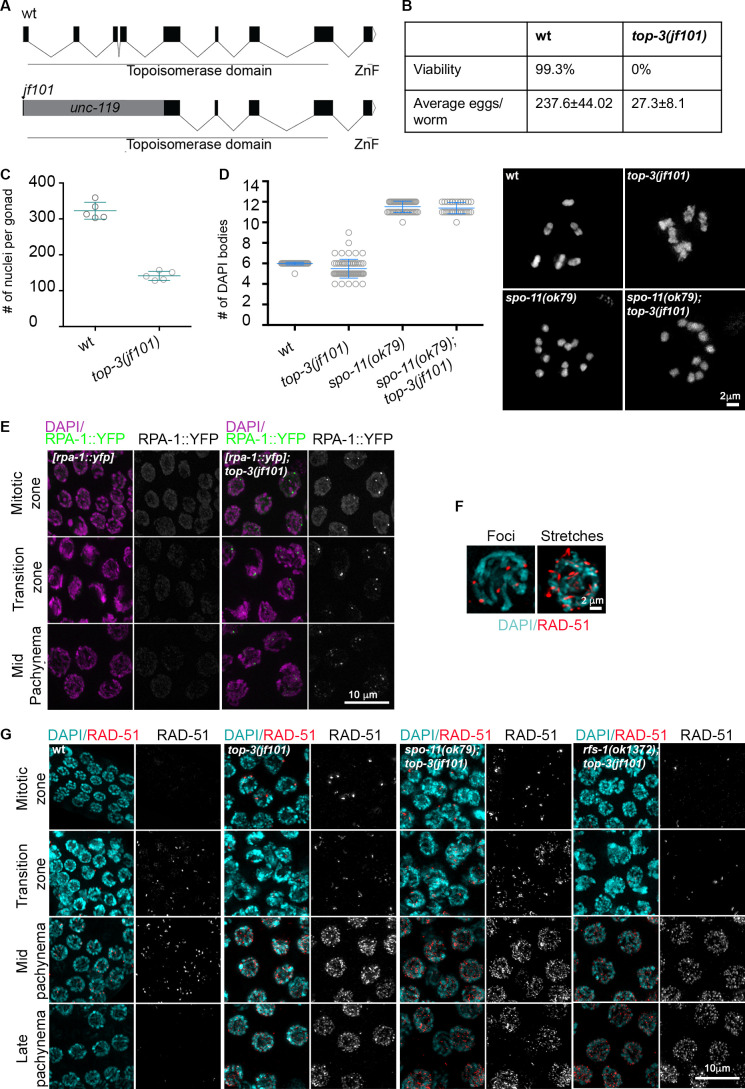
Figure 1.
Germline phenotype of the top-3 mutant. (A) Schematic representation of the top-3 gene, indicating the conserved topoisomerase domain, the RGF zinc finger (ZnF) motif, and introns and exons. In the jf101 allele, the ORF is disrupted by insertion of the unc-119 locus directly after the start codon, resulting in the deletion of 171 aa in the N terminus. (B) Hatch rates and brood sizes of the top-3(jf101) mutants (n = 15 worms) and wt (n = 16 worms). (C) Quantification of the total number of germline nuclei (from the mitotic region to late pachynema). Scatter plots indicate the mean ± SD number. Five gonads were quantified for each genotype. wt, 322.8 ± 23.7; and top-3(jf101), 141.4 ± 12.5. (D) Quantification of DAPI bodies in the −1 diakinesis oocyte: wt,6 ± 0.06, n = 57; top-3(jf101), 5.4 ± 0.8, n = 65; spo-11(ok79), 11.5 ± 0.5, n = 54; and top-3(jf101); spo-11(ok79), 11.4 ± 0.6, n = 33. n is the number of oocytes. The scatter plot indicates the mean ± SD. Inserts show representative images of DAPI-stained diakinesis nuclei of the indicated genotypes. See Fig. S1 A for an additional phenotypic analysis. (E) Representative images of [RPA-1::YFP] localization at different stages of meiotic prophase I in the indicated genotypes. Gonads were stained with DAPI (magenta) and endogenous YFP (green). (F) Higher magnification images showing RAD-51 stretches in top-3 mutants (right) and RAD-51 foci in the wt (left). (G) Representative images of RAD-51 foci localization at different stages of meiotic prophase I for the indicated genotypes. Gonads were stained with DAPI (cyan) and an anti-RAD-51 antibody (red). wt, wild-type.