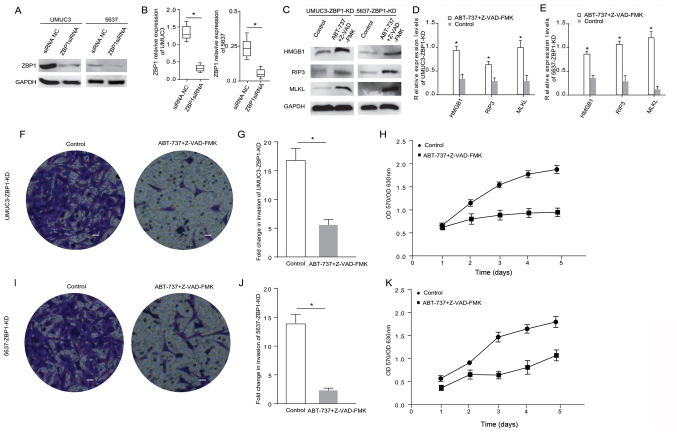
Figure 4.
ABT-737 induces cancer cell necrosis and inhibits cell viability and invasion when the ZBP1 gene is knocked down in bladder cancer cells. (A) Expression levels of ZBP1 were analyzed in UMUC3 and 5637 cells via western blotting after treatment with ZBP1 siRNA for 12 h, and the results were (B) semi-quantified. (C) Protein expression levels of HMGB1, RIP3 and MLKL were analyzed in ZBP1-KD UMUC3 and ZBP1-KD 5637 cells treated with Z-VAD-FMK combined with ABT-737 for 12 h. The results were semi-quantified in (D) UMUC3 and (E) 5637 cells. (F) Transwell invasion assays were performed with UMUC3-KD cells. (G) Quantification of Transwell assay results. (H) MTT assays were performed to examine the viability of ZBP1-KD UMUC3 cells treated with Z-VAD-FMK combined with ABT-737 for 12 h. (I) Transwell invasion assays were performed with ZBP1-KD 5637 cells. (J) Quantification of Transwell assay results. (K) MTT assays were performed to examine the viability of ZBP1-KD 5637 cells treated with Z-VAD-FMK combined with ABT-737 for 12 h. *P<0.05 vs. siRNA NC or control. OD, optical density; scale bar=50 µm; ZBP1, Z-DNA binding protein 1; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; MLKL, mixed-lineage kinase domain-like protein; siRNA, small interfering RNA; NC, negative control; KD, knockdown.