Figure 6. Theoretical model illustrating the role of CMV-specific CX3CR1+ GPR56+ CD57+ (C~G~C) T cells in promoting adipose tissue inflammation and CVD.
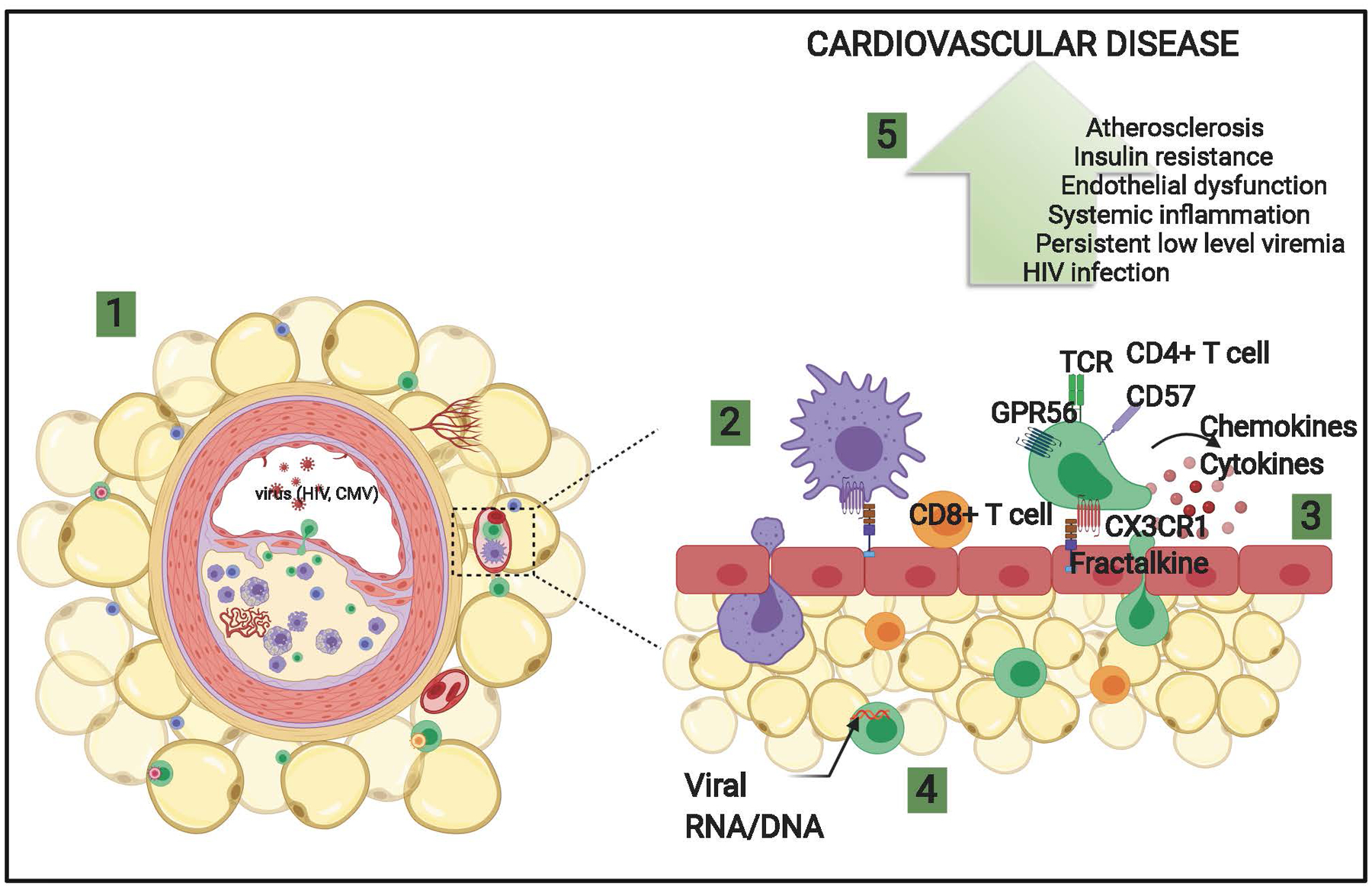
1) Schematic of coronary plaque and perivascular adipose tissue in HIV-positive persons. 2) Peripheral leukocytes expressing CX3CR1 bind to fractalkine/CX3CL1 on endothelial cells and migrate to the perivascular adipose tissue. 3) Inflammatory cytokines and chemokines are expressed by immune cells recruited coronary vessels and perivascular adipose tissue, including virus-specific T cells that disrupt endothelial function and may contribute to plaque deposition in large arteries. 4) Clonal CD4+ (green) and CD8+ memory T cells (orange) predominate in perivascular adipose tissue of HIV-positive persons and are proinflammatory. 5) Increased inflammation, vascular dysfunction, and atherosclerosis contributes to cardiovascular disease.
