Figure 3.
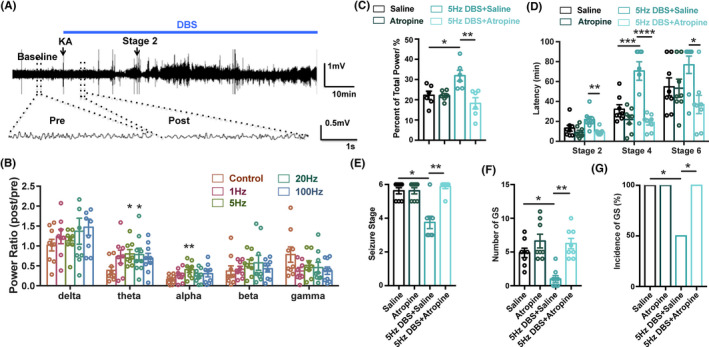
Hippocampal theta rhythm mediates the antiseizure effects of DBS. (A) Experiment scheme for EEG recording and analysis in KA‐induced acute seizure model. (B) The effects of DBS on the spectrum analysis of hippocampal EEG rhythm (n = 8 for each group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared with Sham group, one‐way ANOVA followed by post hoc Dunnett tests). To minimize individual variation, the normalized power ratio in each mouse was calculated through post power (start of DBS) divided by pre power (baseline). (C) Atropine abolished the DBS‐induced increase of theta rhythm (n = 6 for each group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one‐way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test). (D‐G) The effects of DBS on the latency to the different seizure stage (D), seizure stage (E), number of GS (F), and incidence of GS (G) in 1.5‐h observation period in KA‐induced acute seizure model, in the presence of atropine. Atropine was intraperitoneal injected before KA injection, DBS was delivered continuously after KA injection. (n = 8 for each group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, one‐way ANOVA followed by post hoc Bonferroni's test was used for D, non‐parametric Kruskal‐Wallis test followed by post hoc Dunn's tests was used for E, F, chi‐square test was used for G)
