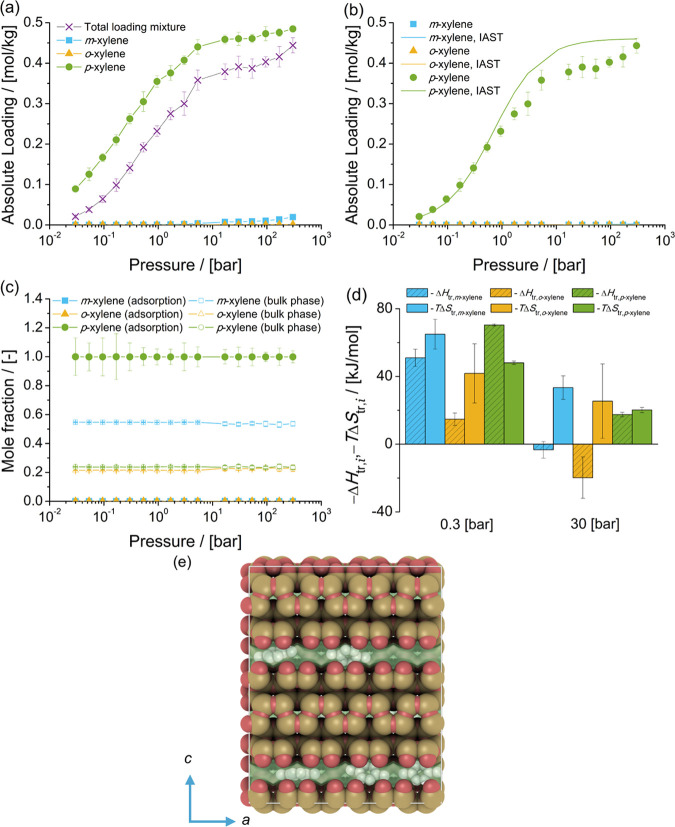
Figure 10.
Adsorption isotherms of xylene isomers as (a) single components (total loading mixture is the sum of the loadings of xylenes from the mixture at chemical equilibrium) and (b) a mixture at chemical equilibrium in MRE-type zeolites at 523 K. (c) Mole fractions of xylene isomers as a function of the total pressure for the mixture at chemical equilibrium adsorbed in the MRE-type zeolite and for the bulk phase. The composition in the bulk phase follows from Figure 1a. (d) Changes in enthalpy ΔHtr,i and entropy TΔStr,i at 523 K due to the transfer of xylene i from the fluid-phase mixture at chemical equilibrium to the MRE-type zeolite at 0.3 and 30 bar. (e) Typical snapshot of the simulation of adsorption of the mixture of xylenes at chemical equilibrium in MRE-type zeolites at 300 bar and 523 K. p-Xylene is shown in gray. The snapshot shows how p-xylene molecules are aligned with the channel of MRE-type zeolites.