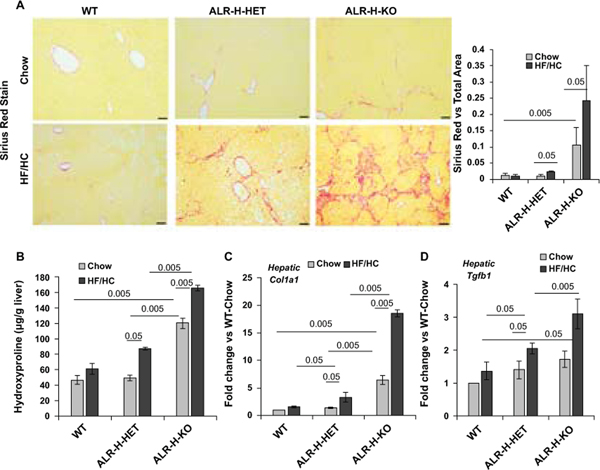
Figure 6: Fibrosis in HF/HC-fed ALR-H-HET and ALR-H-KO mice.
Mice were fed HF/HC diet for 16 weeks. (A) Sirius Red staining (10X magnification) shows bridging fibrosis in ALR-H-KO mice fed chow-diet. After HF/HC feeding, ALR-H-HET mice showed moderate fibrosis whereas ALR-H-KO mice progressed to cirrhosis. No fibrosis was observed in the WT mice fed HF/HC diet. See Figure S5 for more images of Sirius Red-stained liver sections of HF/HC-fed ALR-H-HET and ALR-H-KO mice. Bar graph shows Image J quantification of Sirius Red-stained areas. (B) Hepatic TGFβ expression was already higher in chow-fed ALR-H-HET and ALR-H-KO mice. TGFβ expression did not increase in HF/HC-fed WT mice, but increased in ALR-H-HET and to even greater magnitude in the ALR-H-KO mice after HF/HC feeding. (C and D) Hepatic hydroxyproline content (major amino acid in collagens) and collagen 1 mRNA expression increased in HF/HC-fed ALR-H-HET and ALR-H-KO mice.