Figure 2: JMJD6 associates with AR-V7 expression and a worse prognosis in mCRPC.
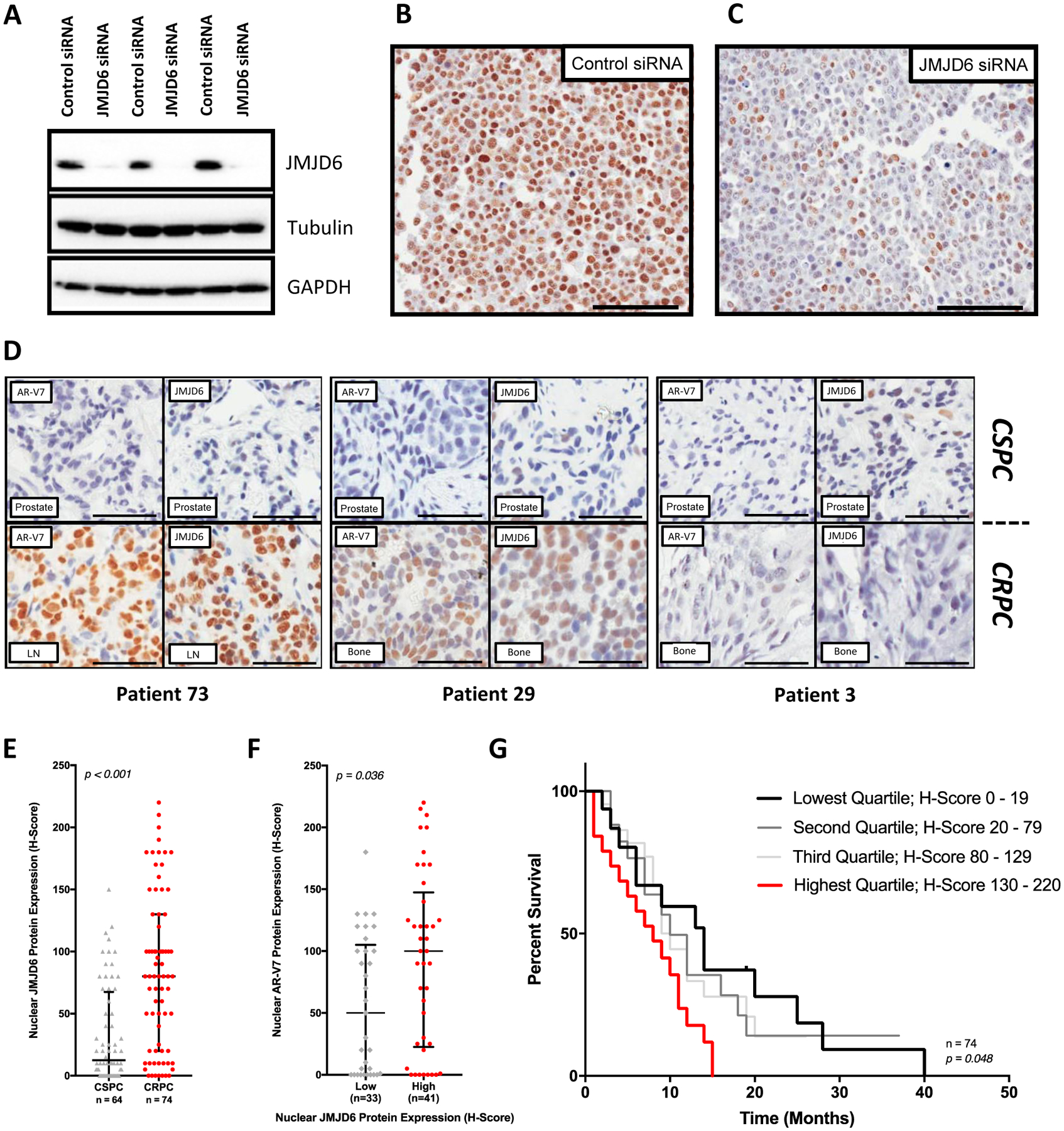
(A) Antibody specificity confirmed by detection of a single band in LNCaP95 whole cell lysates by WB, with downregulation following treatment with pooled JMJD6 siRNA compared to non-targeting control siRNA. (B) Micrograph of LNCaP95 PC cells treated with non-targeting control siRNA demonstrating positive brown nuclear staining for JMJD6. (C) Micrograph of LNCaP95 PC cells treated with pooled JMJD6 siRNA. Demonstrates a marked reduction in JMJD6 protein, with predominately blue, negative staining for JMJD6. (D) Micrographs of IHC analyses for AR-V7 (left) and JMJD6 (right) protein levels in matched, same-patient, diagnostic castration-sensitive (CSPC) (top) and mCRPC (bottom) tissue samples from three different patients (RMH/ICR patient cohort). Scale bars set to 100μm. JMJD6 protein levels in presented tissue samples are similar to AR-V7 levels in mCRPC. (E) Box and whisker plot demonstrating a significant increase (p<0.001) in JMJD6 protein levels (IHC H-Score) in mCRPC biopsies (median H-score [IQR]; CSPC (n=64) 12.5 [0.0–67.5] vs CRPC (n=74) 80 [20.0–130.0]; Wilcoxon rank-sum analysis). (F) Levels of AR-V7 protein significantly higher (p=0.036) in mCRPC tissue samples from patients with high (JMJD6 H-Score ≥ median) mCRPC JMJD6 protein levels (Low 50 [0.0–105.0; n = 33] vs High 100 [22.5–147.5; n = 41]; Mann-Whitney test). (G) Median OS from the time of CRPC tissue biopsy significantly worse in patients with the highest levels of JMJD6 (H-Score > 75th percentile) in their mCRPC tissue sample (n=74, p=0.048; Log-rank test).
