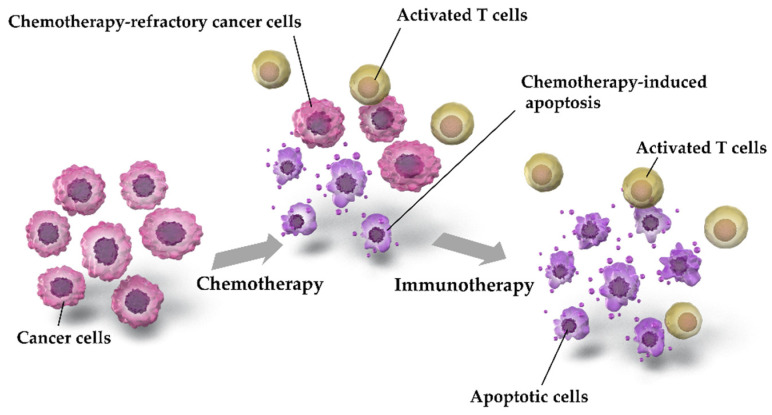
Figure 9.
Possible mechanisms underlying the combination effects of chemotherapy and immunotherapy. Chemotherapy-induced apoptosis of cancer cells leads to the collection of activated T cells. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1)-mediated suppression of anticancer T cells by cancer cells is inhibited by treatment with ICIs, such as Pem, Dur, or Atz, which may restore T cell activation and induce cancer cell apoptosis. Accordingly, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are more effective when used as a combination therapy than when used separately.